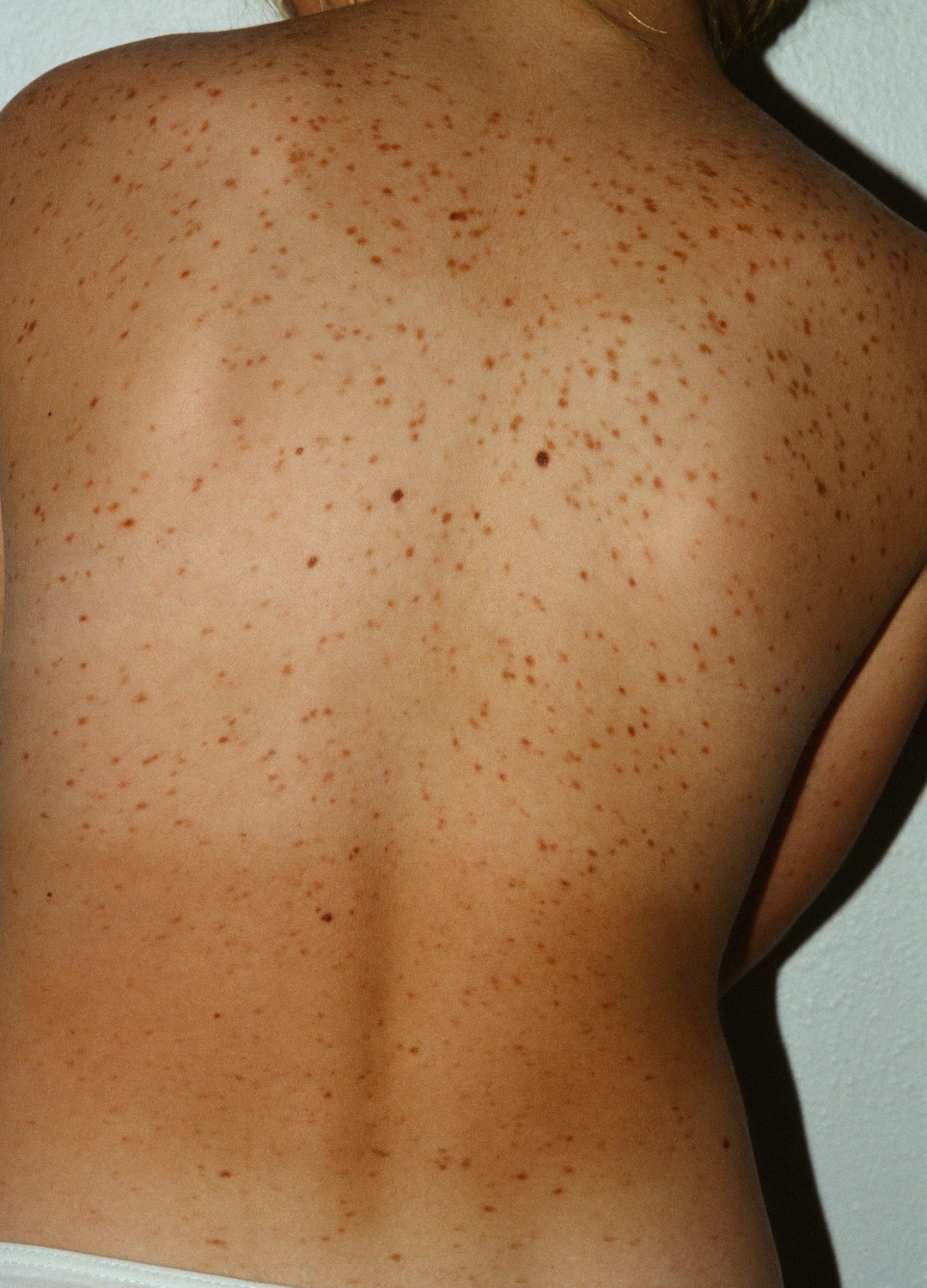
Multiple pigmented macules on back of a 12-year-old girl with UP.

Multiple pigmented macules on back of a 12-year-old girl with UP.
Urticaria Pigmentosa (UP) is a variant of cutaneous mastocytosis in which multiple pigmented macules or papules develop, each overlying a dermal accumulation of mastocytes.
Various patterns of cutaneous mastocytosis occur in children. One extensive review of all cases of pediatric mastocytosis found the following distribution of clinical presentation:
| Disease | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Urticaria pigmentosa | 75% |
| Mastocytoma | 20% |
| Diffuse cutaneous mastocytosis | 5% |
| TMEP | < 1% |
Patients may have a few to several thousand brown macules or papules. The trunk is the most common site, followed by the extremities. The face, scalp, palms, and soles are usually spared. Both children and adults may be affected. Gastrointestinal or systemic histamine effects include diarrhea, stomach pain, flushing, or lightheadedness.
Darier sign (urtication upon stroking) is positive. Adult patients who have presented with typical urticaria pigmentosa may go on to develop systemic mastocytosis as manifested by nodules, flushing, hepatosplenomegaly, and duodenal ulcers. Death secondary to anaphylaxis has been reported in a patient who drank alcohol and then was exposed to winter snow. The pigmentation histologically is basal melanosis. Histamine in vitro stimulates melanocytes suggesting the mechanism of pigmentation. Massive peripheral eosinophilia may rarely be seen.
All patients should have a CBC with differential. Tryptase levels may be measured and may correlate with extent of skin involvement. Bone survey and bone marrow biopsy often shows abnormalities but their significance is unclear. KIT mutation analysis may be considered in an investigational setting.
Urticaria pigmentosa often resolves by puberty, with many lesions disappearing or improving significantly. However, it can persist into adulthood, although symptoms usually lessen over time.
Homepage | Who is Dr. White? | Privacy Policy | FAQs | Use of Images | Contact Dr. White