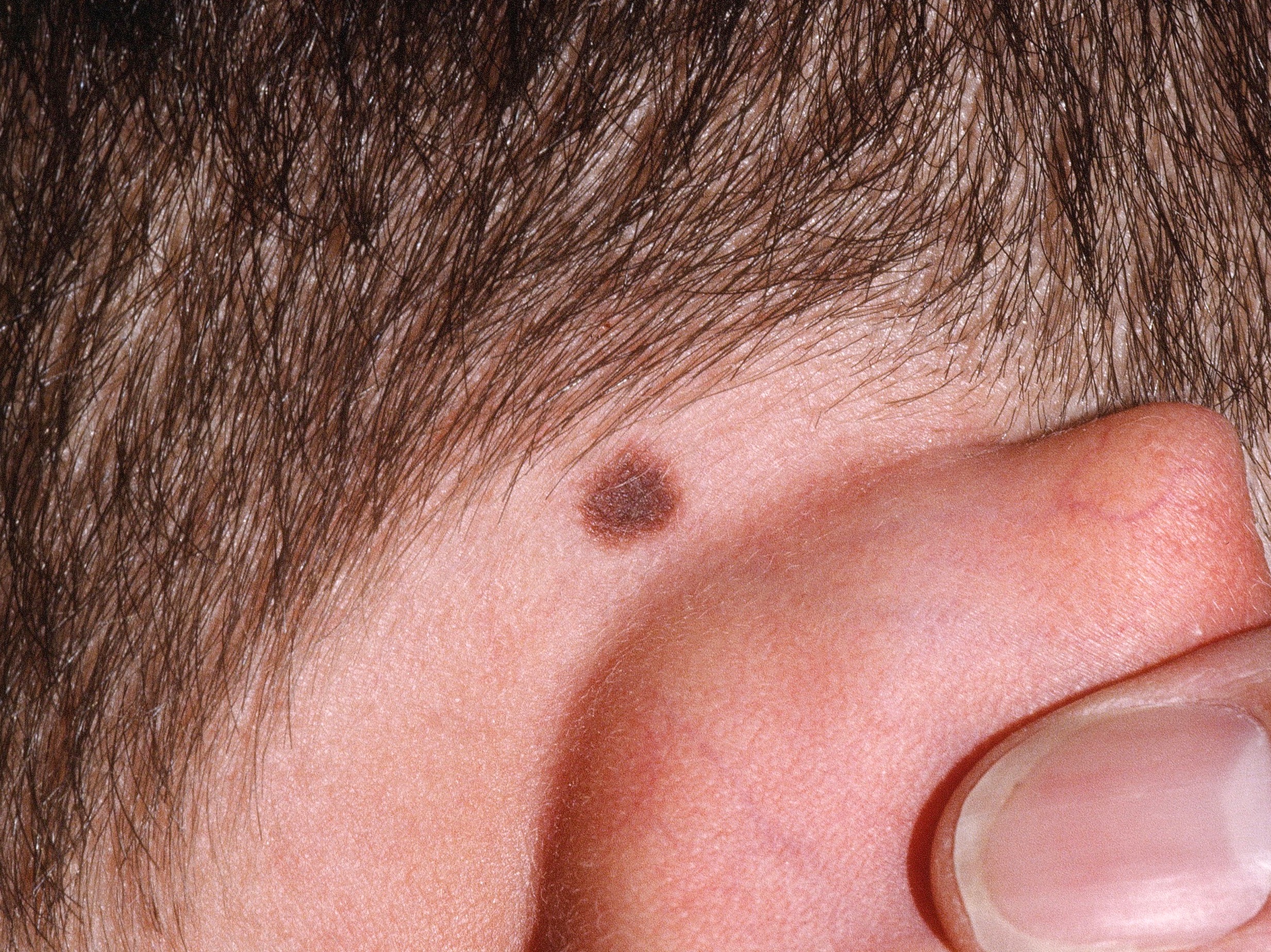
Junctional nevi tend to be round or oval, flat and uniform in color.
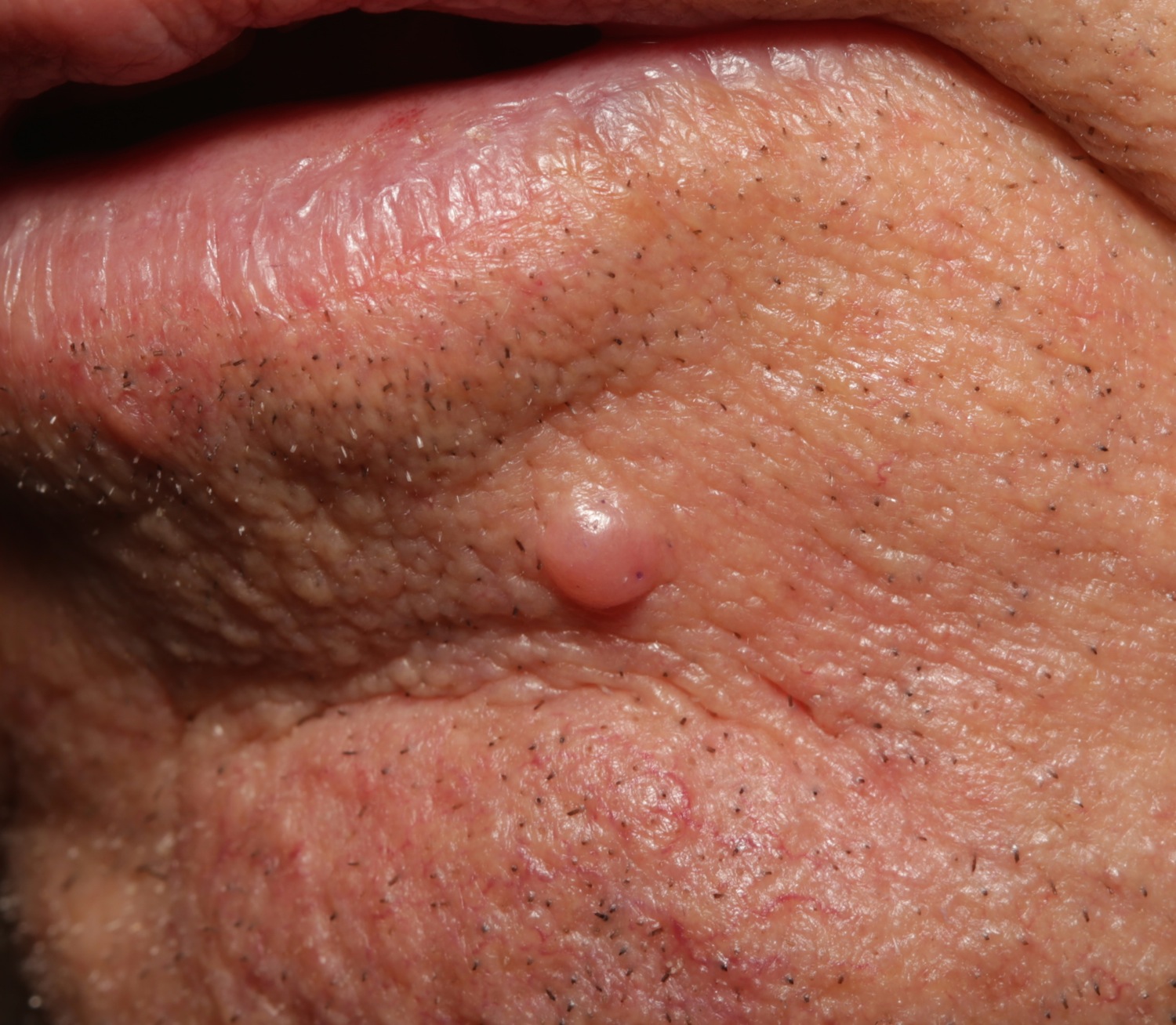
Intradermal nevi are raised, round and typically flesh-colored but they can also be light brown or even dark brown. This one was biopsied to rule out basal cell carcinoma.
MELANOCYTIC NEVI
Acquired melanocytic nevi--or moles--are common, benign growths of the skin. It is critical for patients to be aware of their moles and seek attention if any develop signs of melanoma. In addition, many patients seek removal of these lesions for functional or cosmetic reasons.
- Total number of moles in humans peaks at about age 30-40.
- In a study of white children in Colorado, the total number of moles increased with both chronic sun exposure and number of sunburns.
- The common "life cycle" for a mole is flat and dark in childhood, raised and losing color in adulthood, gone in old age.
- Various studies have used the number of moles (defined as >= 3 mm diameter) on the extremities as a proxy for total nevus count. The risk of melanoma is increased with increased number of extremity moles (as is BCC but not SCC. The highest risk category is seen in those with >= 10 moles on the extremities.
- Traumatizing moles is not a risk factor for melanoma.
- In one study, women with more than 11 nevi [defined as 2 mm or greater in diameter] on the right arm were approximately nine times more likely to have more than 100 nevi (which is a predictor of increased risk of melanoma.)
- Women aged 40-65 with more than 15 moles on their left arms were found to have a 35% increased risk of breast cancer than women with no moles.
- Only about 30% of melanomas arise from pre-existing nevi.
- Moles on the hands and feet are not at increased risk for melanoma than moles elsewhere.
See also eclipse, blue and halo.
Clinical
Nevomelanocytic nevi come in all shapes and sizes. Early in their life cycle, they tend to be flat and dark (junctional nevus). As the patient ages, the nevi tend to raise up and lose their color (intradermal nevus). Late in life, nevi may disappear altogether. Nevi are common on the upper back, probably because that area gets significant sun exposure. In one study, nevi were most common on the outer forearms, followed by the outer upper arms, neck and face. Larger nevi were most prevalent on the intermittently exposed skin of the trunk. In studies that count nevi, the peak age for the most number of nevi ranges from 30-40 years of age.
Uniform Nomenclature
It has been suggested to define more clearly the terms used to describe pigmented lesions, much the way radiologists have unified their terminology .
- Shape: symmetric (round or oval) or asymmetric.
- Border: Well-circumscribed (sharp edges) or poorly circumscribed (indistinct edges or edges which are lobulated or spiculated)
- Color: Uniform or Non-uniform (globular, focally non-uniform)
- Pigment pattern: Central, Divided, Eccentric, Peripheral, Speckled
- Diameter: Measure longest axis and then the axis perpendicular to that.
It seems like further terms describing how raised (or flat) the lesion is would be in order.
Moles and Melanoma
Counting the number of moles >= 3 mm on both arms from the elbow to the wrist is a good screen for the need for a complete skin exam. Any person with 3 or more such moles is likely to have a high total body nevus count and a higher risk of melanoma. Each additional mole conveys a 1.20 hazard risk for melanoma death.
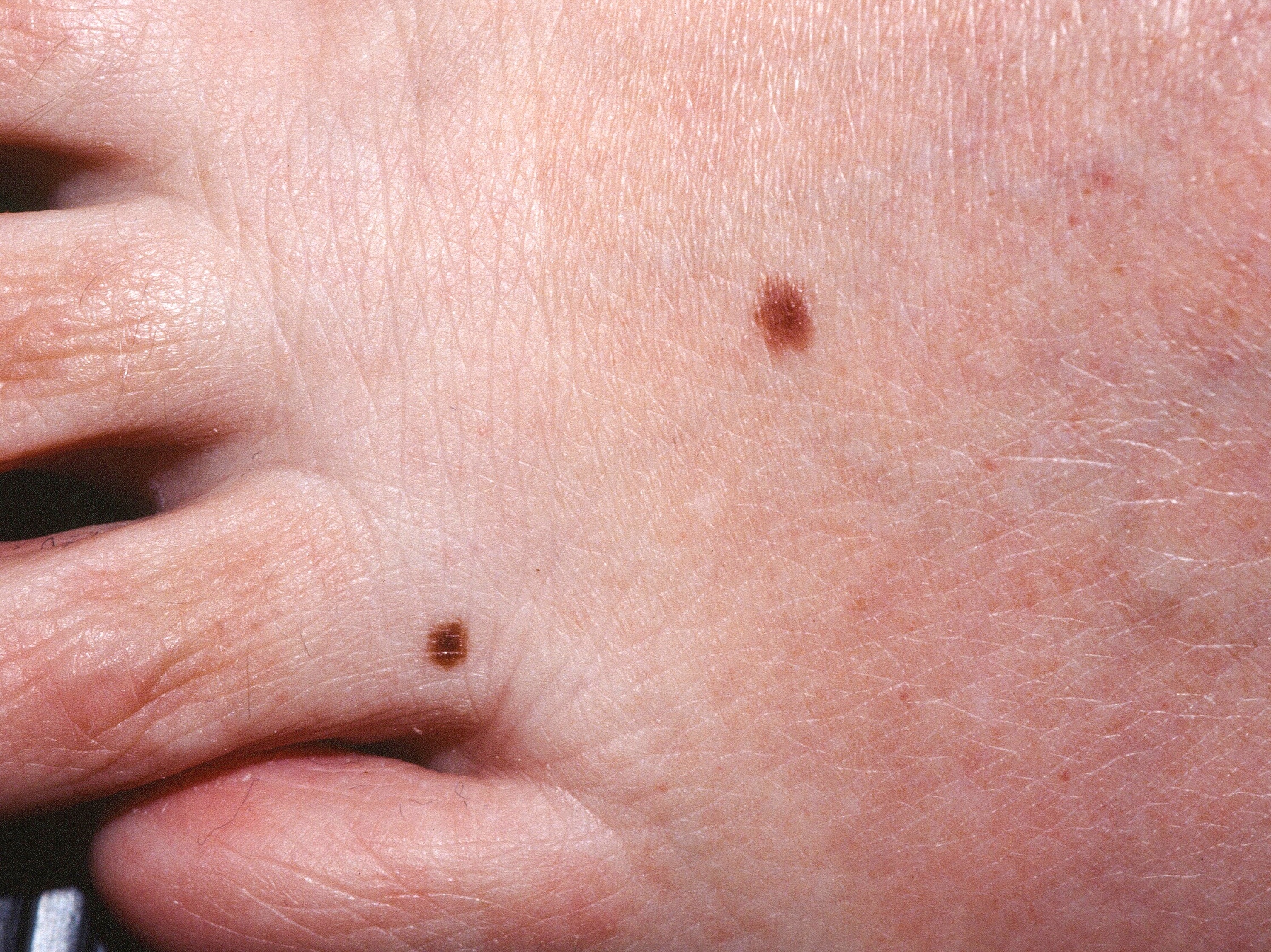
Two benign nevi on the foot.
 q
Benign nevi tend to be round or oval and uniform in color.
q
Benign nevi tend to be round or oval and uniform in color.
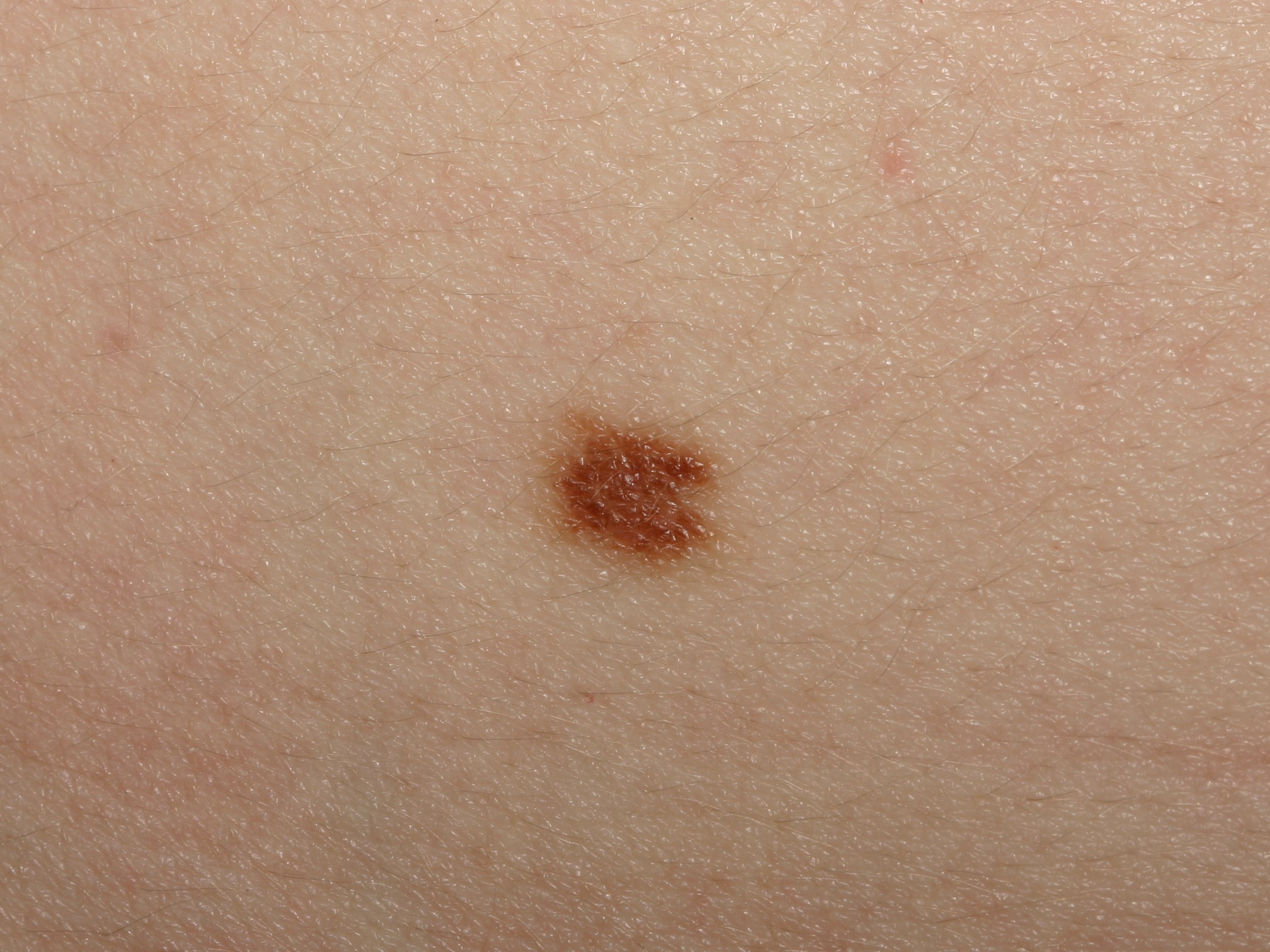
This benign nevus has a small notch on the right side, but the lesion is small and uniform in color.

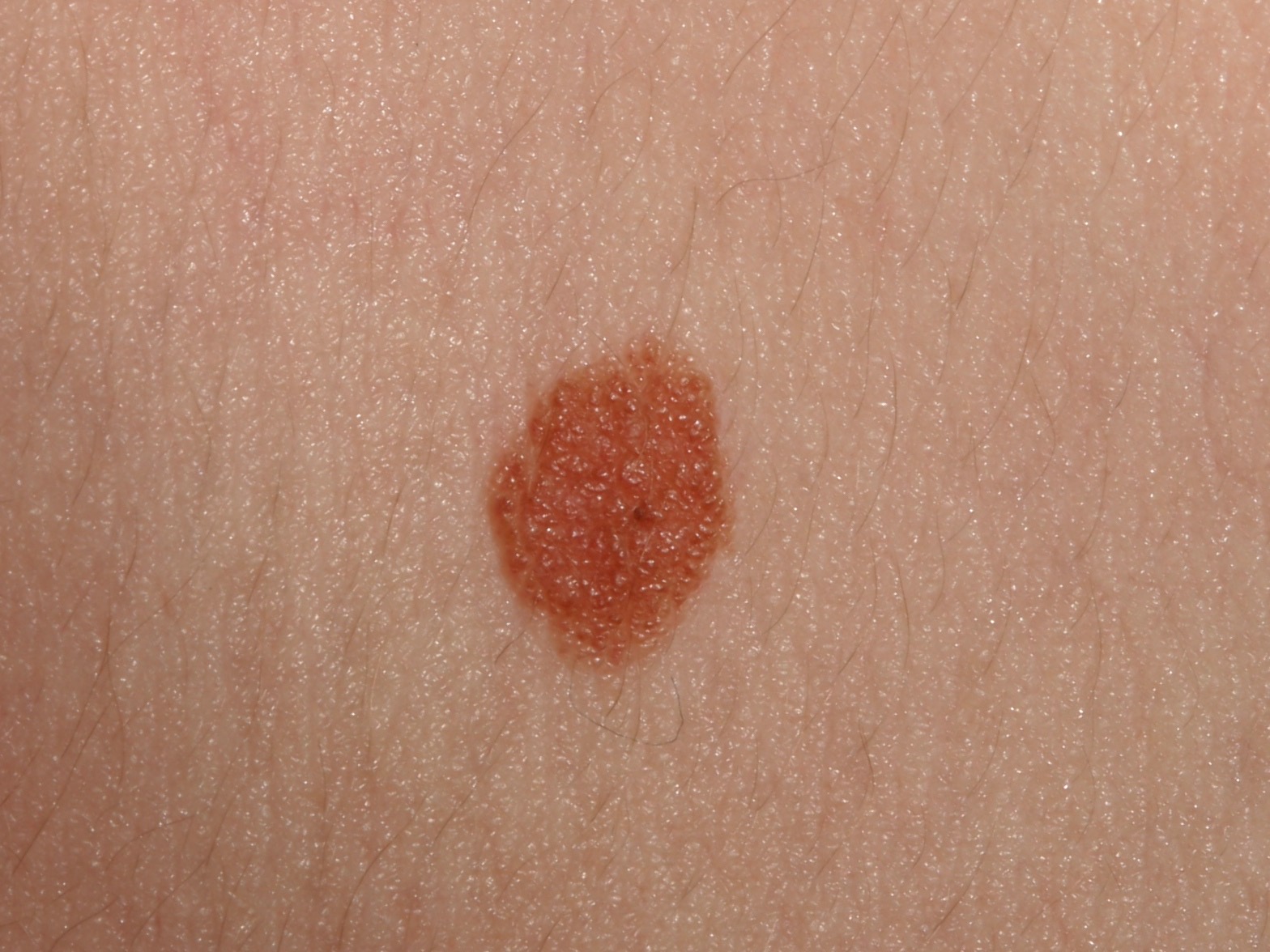
A little bit of blood in this intradermal nevus.
RegionalDerm
Homepage | Who is Dr. White? | Privacy Policy | FAQs | Use of Images | Contact Dr. White
It is not the intention of RegionalDerm.com to provide specific medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. RegionalDerm.com only intends to provide users with information regarding various medical conditions for educational purposes and will not provide specific medical advice. Information on RegionalDerm.com is not intended as a substitute for seeking medical treatment and you should always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider for diagnosis and for answers to your individual questions. Information contained on RegionalDerm.com should never cause you to disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking treatment. If you live in the United States and believe you are having a medical emergency call 911 immediately.



 q
Benign nevi tend to be round or oval and uniform in color.
q
Benign nevi tend to be round or oval and uniform in color. 
