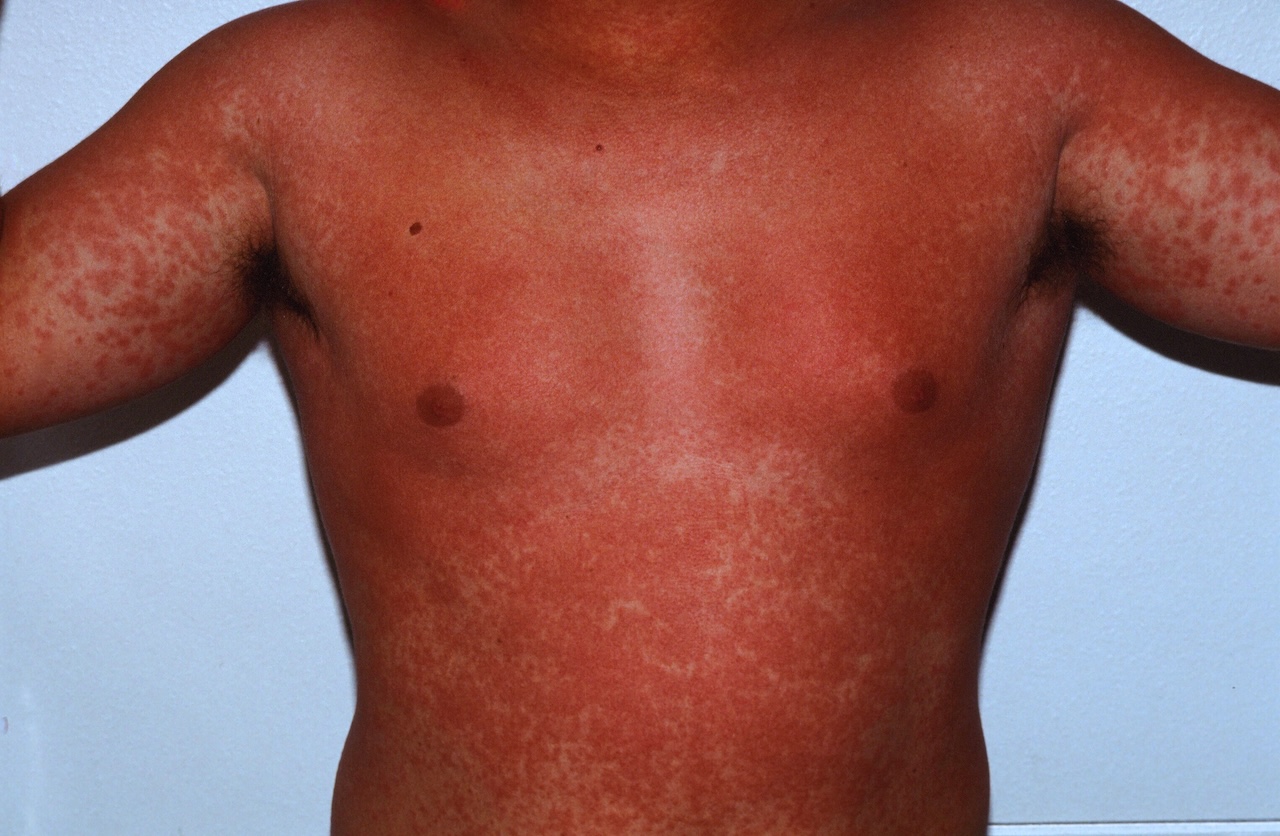
Drug eruptions are common and represent the classic maculopapular eruption.
The classic presentation is a diffuse maculopapular eruption. Many variants occur including bullous, eczematous, pustular, photoexposed and severe with skin sloughing (toxic epidermal necrolysis). Some patients may develop a drug eruption with preference for the flexures.
A maculopapular drug eruption may occur associated with infectious mononucleosis and antibiotic use (e.g. ampicillin, amoxicillin, methicillin, pivampicillin, talampicillin and azithromycin). It is thought that this represents a true antibiotic reaction in the setting of altered immune state resulting from the EBV infection.
| Sign and Symptoms | Consideration |
|---|---|
| No mucous (eye, mouth) involvement, bulla, pustules, or necrosis, etc. | Classic Drug Eruption (discussed here) |
| Onset 2-6 weeks after exposure, hypereosinophilia, liver involvement | DRESS Syndrome |
| Mucosal Invovlement | SJS/TEN |
| Bulla | Bullous Drug Eruption, Bullous EM, SJS/TEN |
| Pustules | AGEP, Pustular Psoriasis |
| Sloughing of Skin | TEN |
| Purpura, Necrosis | Vasculitis |
In the setting of a classic urticaria like maculopapular rash soon after exposure to a new agent, the diagnosis is straightforward. When in doubt, a skin biopsy may be performed. Many will get a CBC, LFTs and u.a.
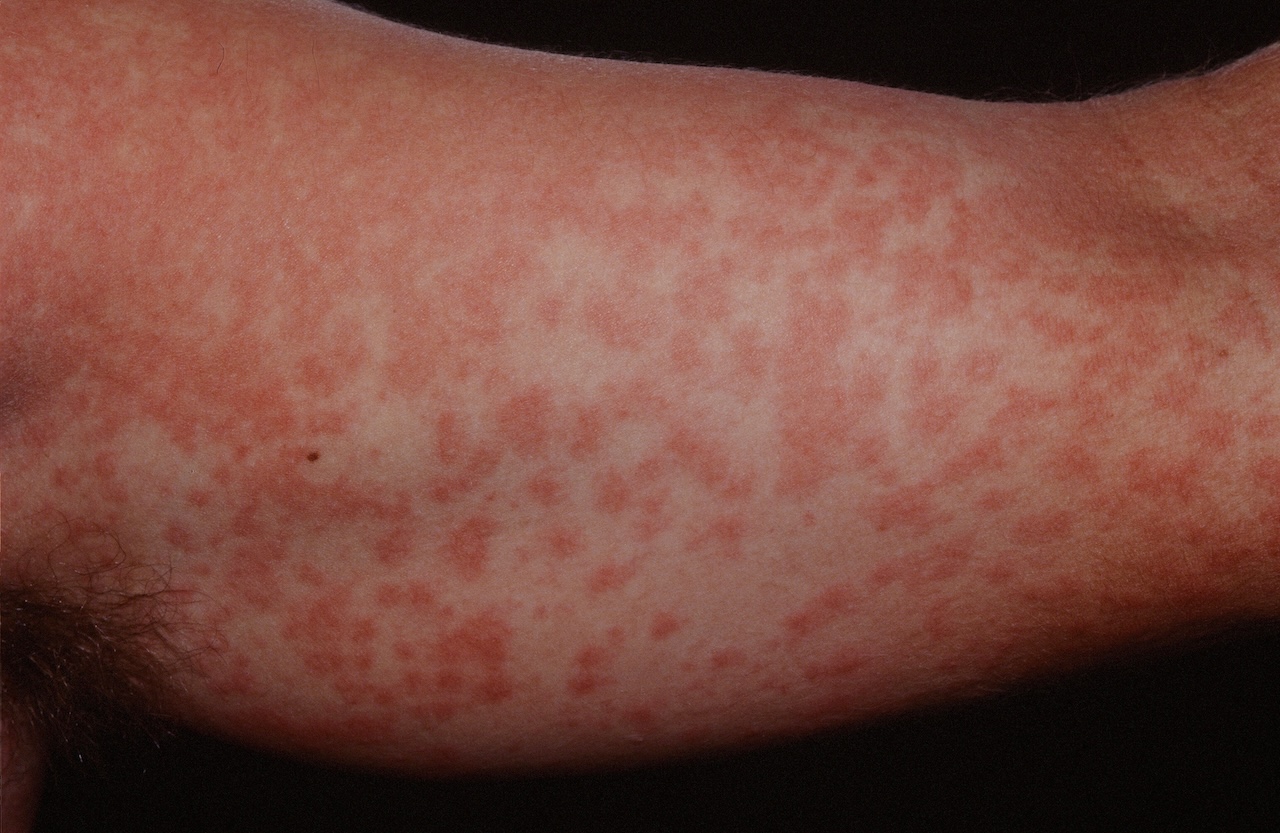
The classic maculopapular rash of a drug eruption.
Homepage | Who is Dr. White? | Privacy Policy | FAQs | Use of Images | Contact Dr. White