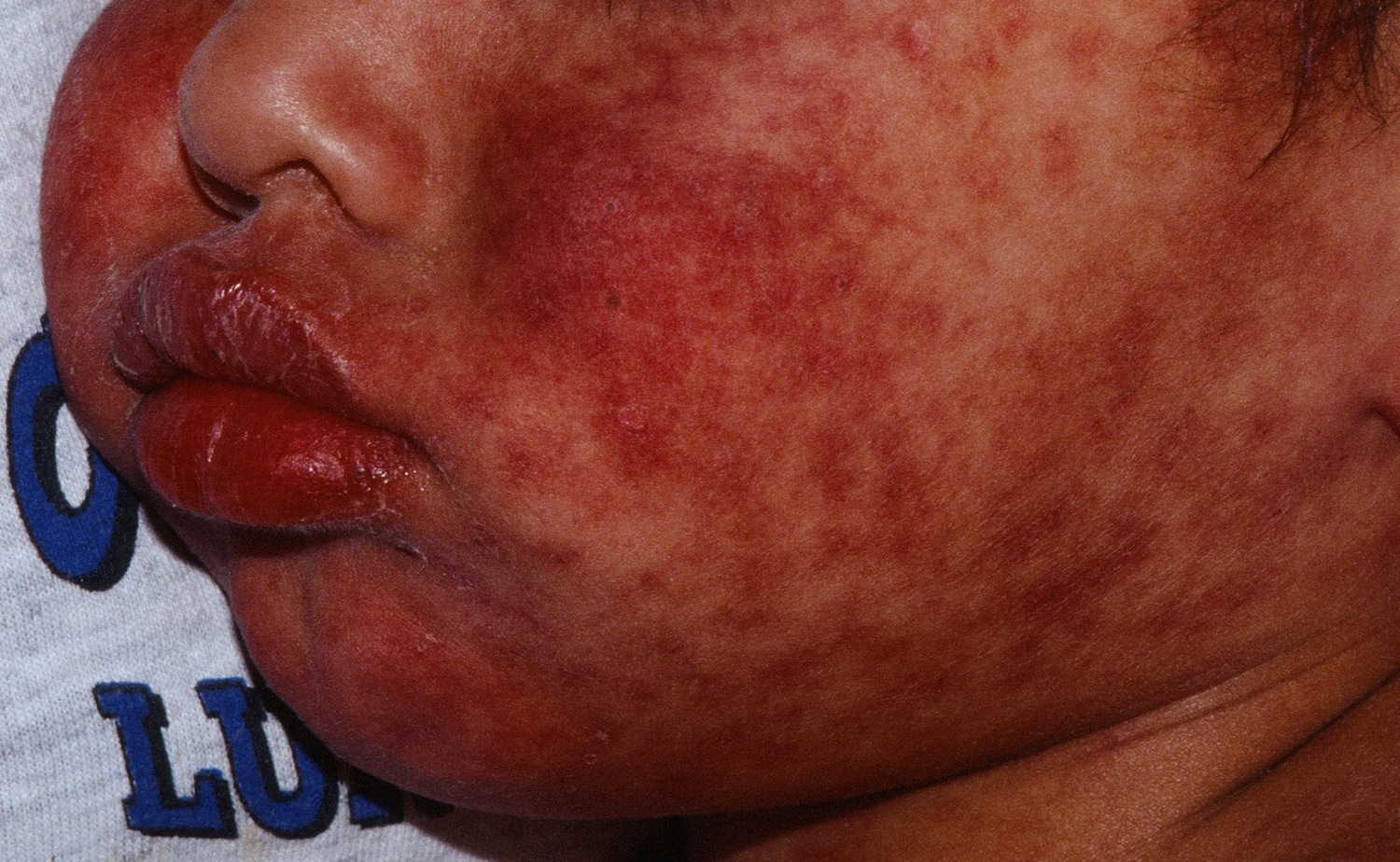
 Facial edema and swollen lips are typical. Pictured is a child reacting to an anticonvulsant.
Facial edema and swollen lips are typical. Pictured is a child reacting to an anticonvulsant.
 Facial edema and swollen lips are typical. Pictured is a child reacting to an anticonvulsant.
Facial edema and swollen lips are typical. Pictured is a child reacting to an anticonvulsant.
DRESS syndrome (Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms) is a rare, potentially life-threatening adverse reaction to medication. Compared with the classic drug eruption, DRESS has a later onset, e.g., 2-6 weeks after exposure, and the patient tends to have facial swelling, a fever and internal organ involvement.
The patient complains of fever and a diffuse red maculopapular rash. There may be significant facial edema. Often the patient will say, "My face is swollen. I don't look like myself". Periocular sparing by the rash is typical. Cervical lymphadenopathy may be prominent. Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) can occur early. Liver involvement may be of the form of elevated LFTs or hepatomegaly. In one study the latency period between drug intake and the onset of symptoms varied from 7 to 90 days with an average of 27.2 days.
Some patients with DRESS develop a pustular eruption and AGEP features without receiving an AGEP diagnosis; these patients may represent a DRESS phenotype with an extended clinical course.
CMV reactivation is a key risk factor for severe complications and death. In one study, 11/55 patients with DRESS had CMV activation. The average onset of CMV antigenemia detection was 27 days after onset of DRESS symptoms. CMV+ DRESS patients tended to be older (e.g., > 60 years), had more severe complications (GI bleeding, sepsis, renal dysfunction, myocarditis) and more likely to die. These complications often occurred soon after CMV activation, (e.g., 6 days). The authors theorized that the use of pulsed prednisone may be related to later development of CMV reactivation via rapid immune recovery. To prevent a rapid immune recovery, the authors recommend that systemic corticosteroids be initiated at a sufficient dose of 40 to 60 mg per day prednisone and be followed by a gradual dose reduction of prednisone at least over >8 weeks. Tapering more gradually over a prolonged period is recommended to achieve the optimum therapeutic result in patients with DRESS.
Anti-CMV therapy is recommended using either ganciclovir (GC) or valganciclovir (VGCV) the moment CMV reactivation is detected. Fatal outcomes were found exclusively in CMV positive cases, especially those in whom anti CMV therapy was initiated >= 3 days after the detection of CMV reactivation.
DRESS is defined as
A workup may include complete drug history, physical and ROS, CBC with diff (looking for eosinophilia), LFTs and creatinine.
Compared with Stevens-Johnsone Syndrome, DRESS shows more:
If there is any concern about DRESS in a patient with a maculopapular rash, blood work to include CBC, LFTs and creatinine are mandatory.
Homepage | Who is Dr. White? | Privacy Policy | FAQs | Use of Images | Contact Dr. White