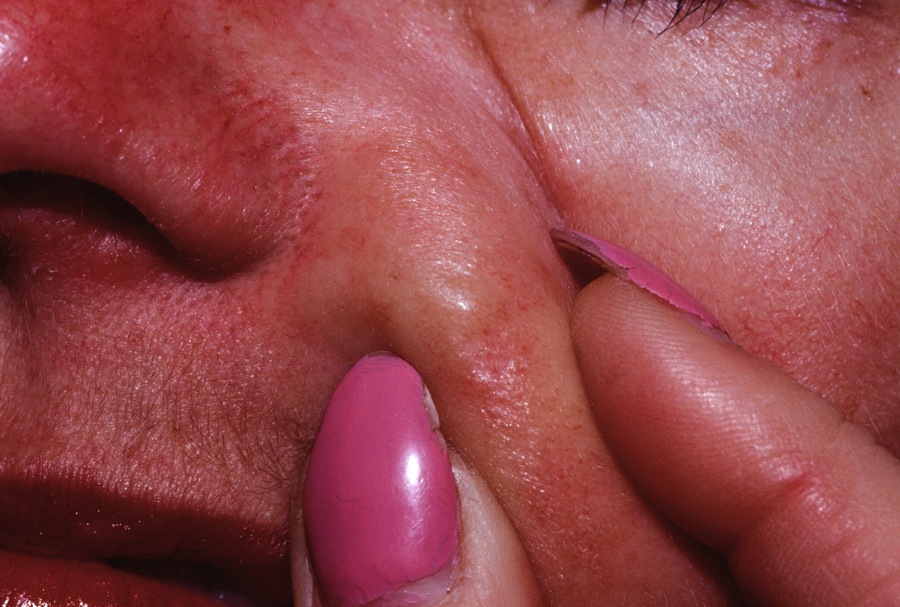
A yellowish plaque on the face. This solitary lesion is typical of the benign type of Alopecia mucinosa.

A yellowish plaque on the face. This solitary lesion is typical of the benign type of Alopecia mucinosa.
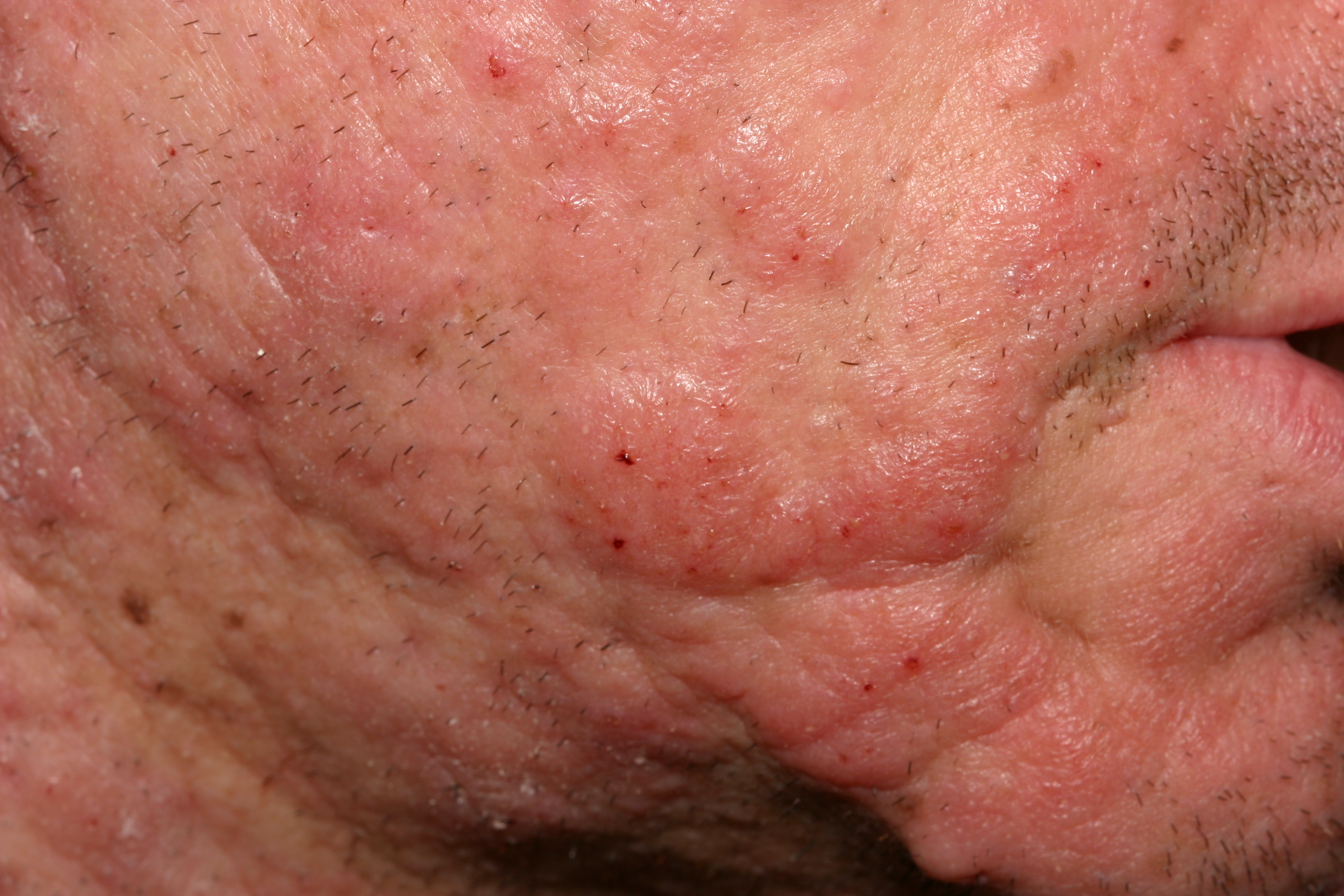
This patient with follicular mucinosis histologically had confirmed CTCL. The skin involvement was extensive and progressive.
Two types of alopecia mucinosa (AM) are seen: a benign type and one associated with CTCL or Hodgkins lymphoma. As a generality, the benign type affects the head and neck, occurs in people under 30, and the lesions are either single or few. The histologic term often used is follicular mucinosis.
Flesh to erythematous colored, follicular papules which may coalesce into plaques most common on the face are characteristic. Alopecia may occur in the lesion.
Differentiating between benign and malignant (mycosis fungoides-associated) alopecia mucinosa is challenging, requiring careful histological analysis, but no single criterion is definitive. While benign cases show infiltrates confined to follicular areas, mycosis fungoides often involves atypical cells and epidermal invasion.
Benign AM often presents as localized, erythematous plaques or patches without hair, primarily on the scalp, neck, and face. Malignant AM can present similarly, but may also show systemic symptoms or features typical of mycosis fungoides, such as atypical skin lesions, lymphocytosis, or Pautrier microabscesses.
Homepage | Who is Dr. White? | Privacy Policy | FAQs | Use of Images | Contact Dr. White