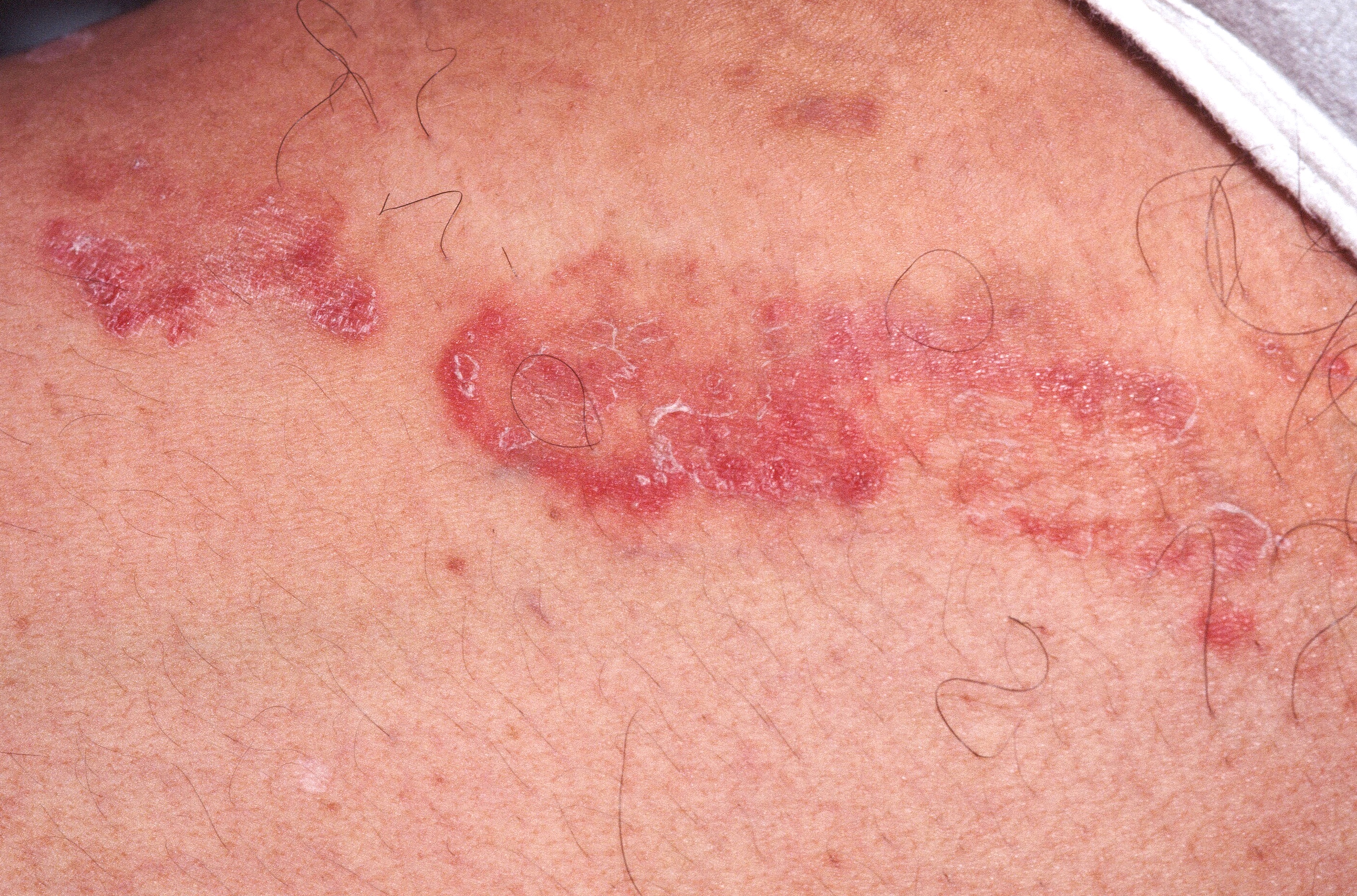
A red, scaly rash in the groin.
TINEA CRURIS
Tinea Cruris (TC) is a fungal infection of the groin, usually by a dermatophyte.
- Look for the characteristic annular, red, scaly border.
- Be careful not to confuse tinea cruris with intertrigo.
- Tinea cruris is more common in men as the scrotal skin, pressed against the thigh, provides for a warm, moist environment in which the fungus may grow.
- Both dermatophyte and Candida may be causative.
- For more (explicit-NSFW) pictures, see gallery.
Clinical
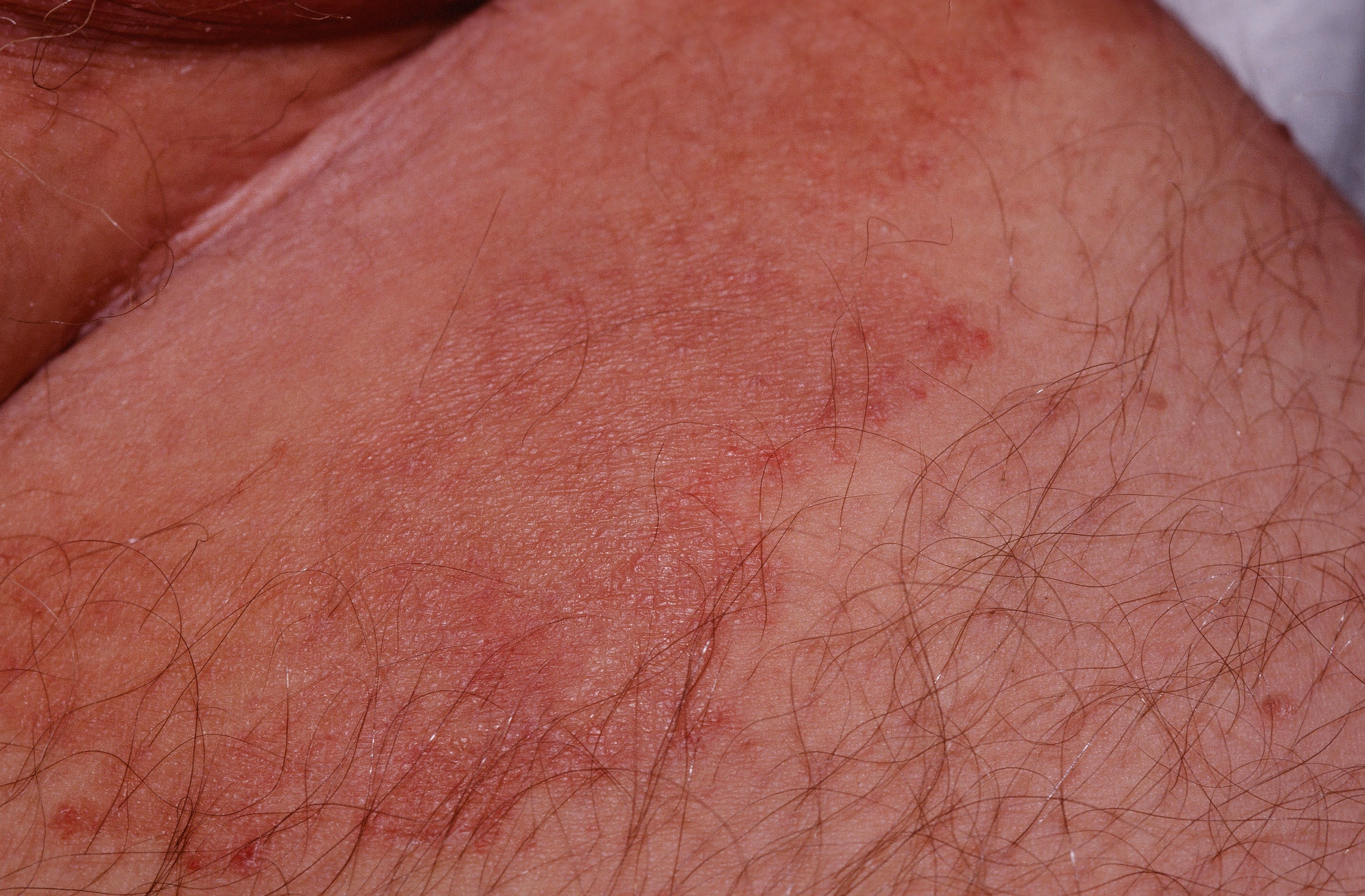
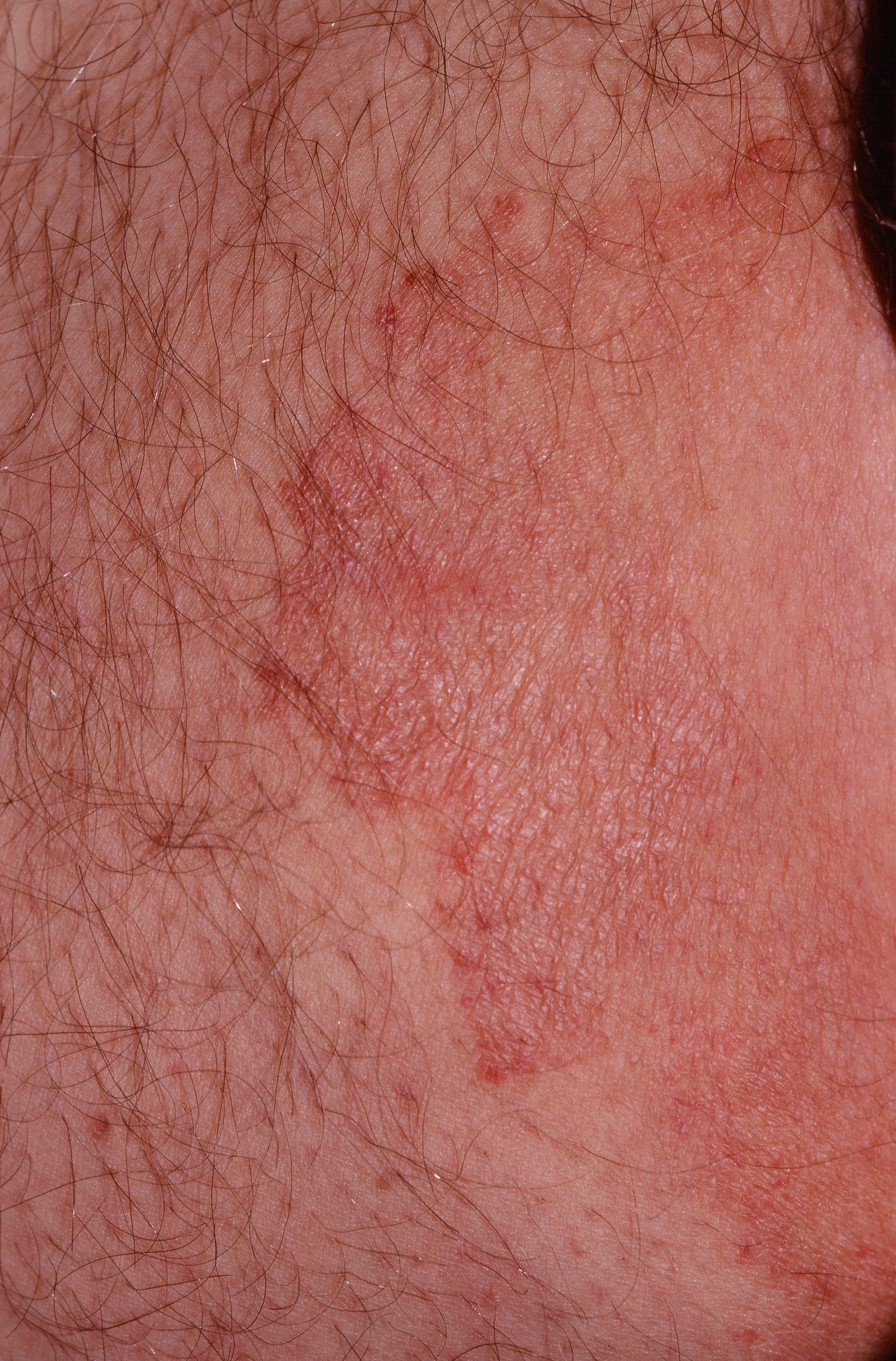
Red, scaly annular lesions in the groin are typical. The condition commonly extends to the buttocks. If a dermatophyte is causative, a red, scaly rash with a raised, "active", border is typical. With Candida, intense erythema with satellite pustules is seen. The patient complains primarily of itch. KOH examination is positive.
x
RegionalDerm
Homepage | Who is Dr. White? | Privacy Policy | FAQs | Use of Images | Contact Dr. White
It is not the intention of RegionalDerm.com to provide specific medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. RegionalDerm.com only intends to provide users with information regarding various medical conditions for educational purposes and will not provide specific medical advice. Information on RegionalDerm.com is not intended as a substitute for seeking medical treatment and you should always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider for diagnosis and for answers to your individual questions. Information contained on RegionalDerm.com should never cause you to disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking treatment. If you live in the United States and believe you are having a medical emergency call 911 immediately.
