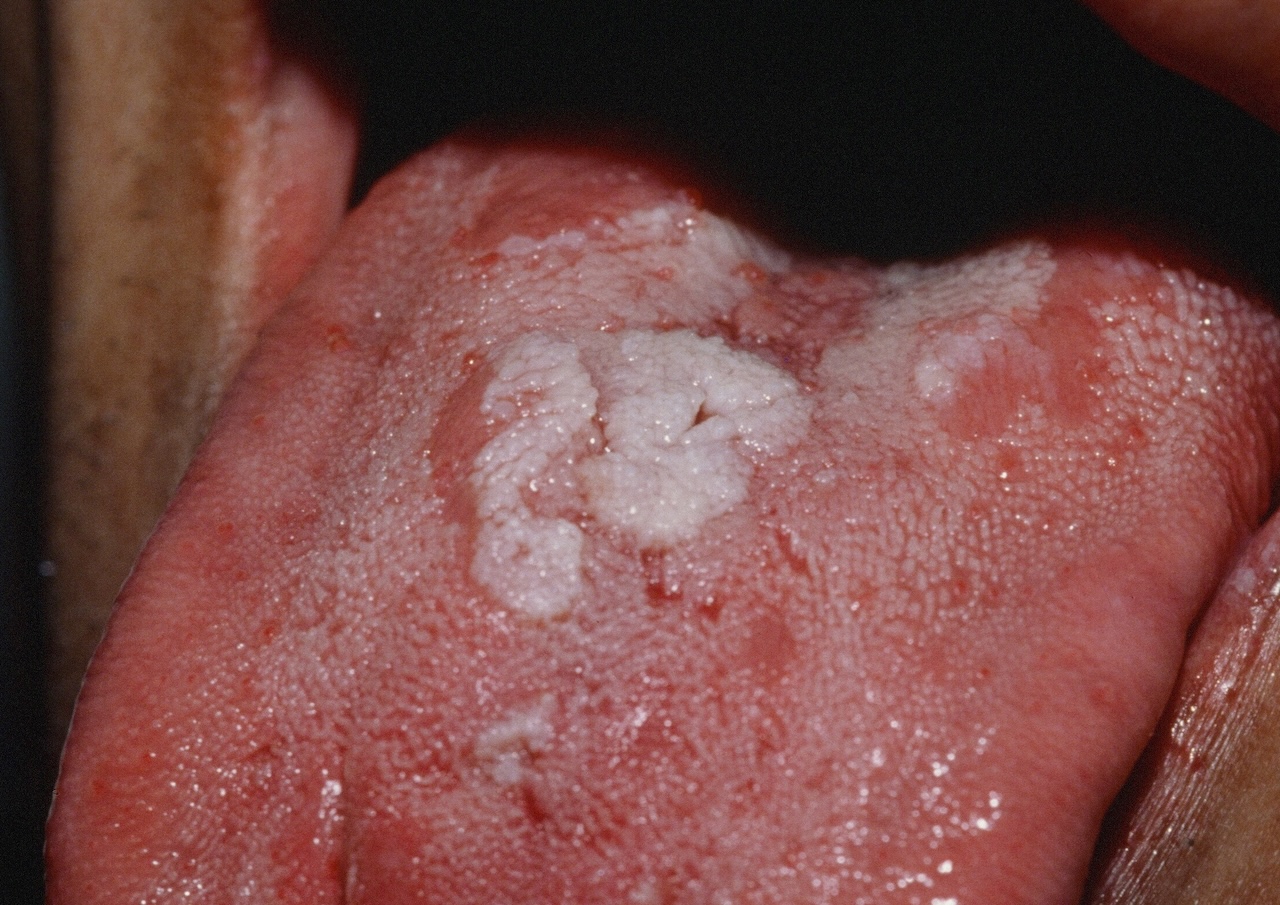
SECONDARY SYPHILIS
About 8 weeks after the primary infection, lesions of secondary syphilis may develop.
Clinical
The rash of secondary syphilis is diffuse and often involves the palms and soles. Lesions are symmetric and coppery red in color. Itch is uncommon. There is no herald patch as in pityriasis rosea. Many morphologies are possible including macular (roseolar), papular, papulosquamous, annular, nodular, pustular, and ulcerative. Other changes include moth-eaten alopecia, alopecia of the eyebrows, condyloma lata (moist plaques occurring perianally and genitally, mucous patches, paronychia, and split papules at the corners of the mouth.
Rarely, secondary syphilis can appear like PLEVA.
Outline
- Prodromal (weight loss, fever, headache, sore conjunctivitis, arthralgias, myalgias) + LAD
- Early (10%): generalized non-pruritic eruption, roseola-like, discrete macules on flanks and shoulders
- Late (70%): generalized maculopapular and papulosquamous eruptions with corymbose arrangement (satellite papules around a larger central lesion), polymorphic in successive waves
- Localized syphilids
- Palms and soles: collarette of Biett
- Anogenital: condylomata lata
- Seborrheic: "corona veneris" hairline
- Chest: "necklace of Venus" hypopigmented macules
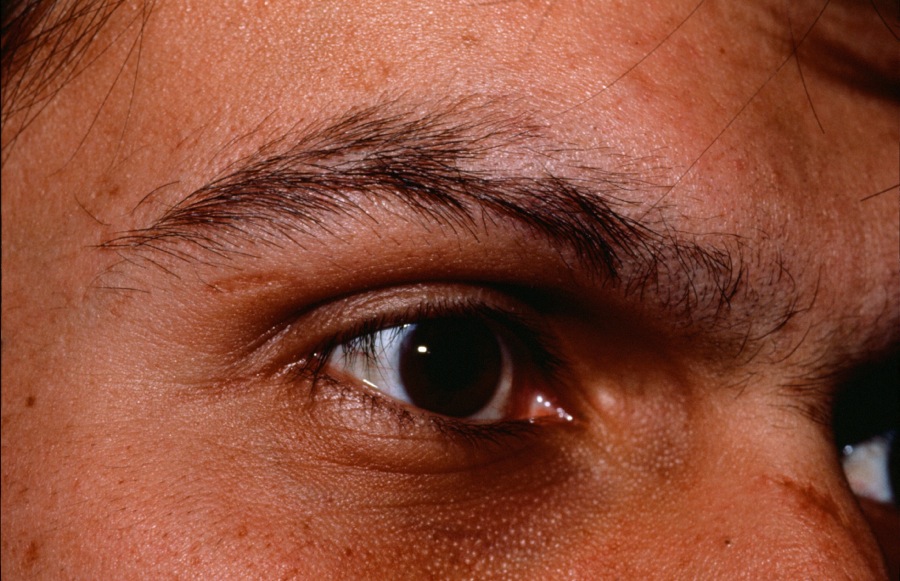
Loss of eyebrow hair.
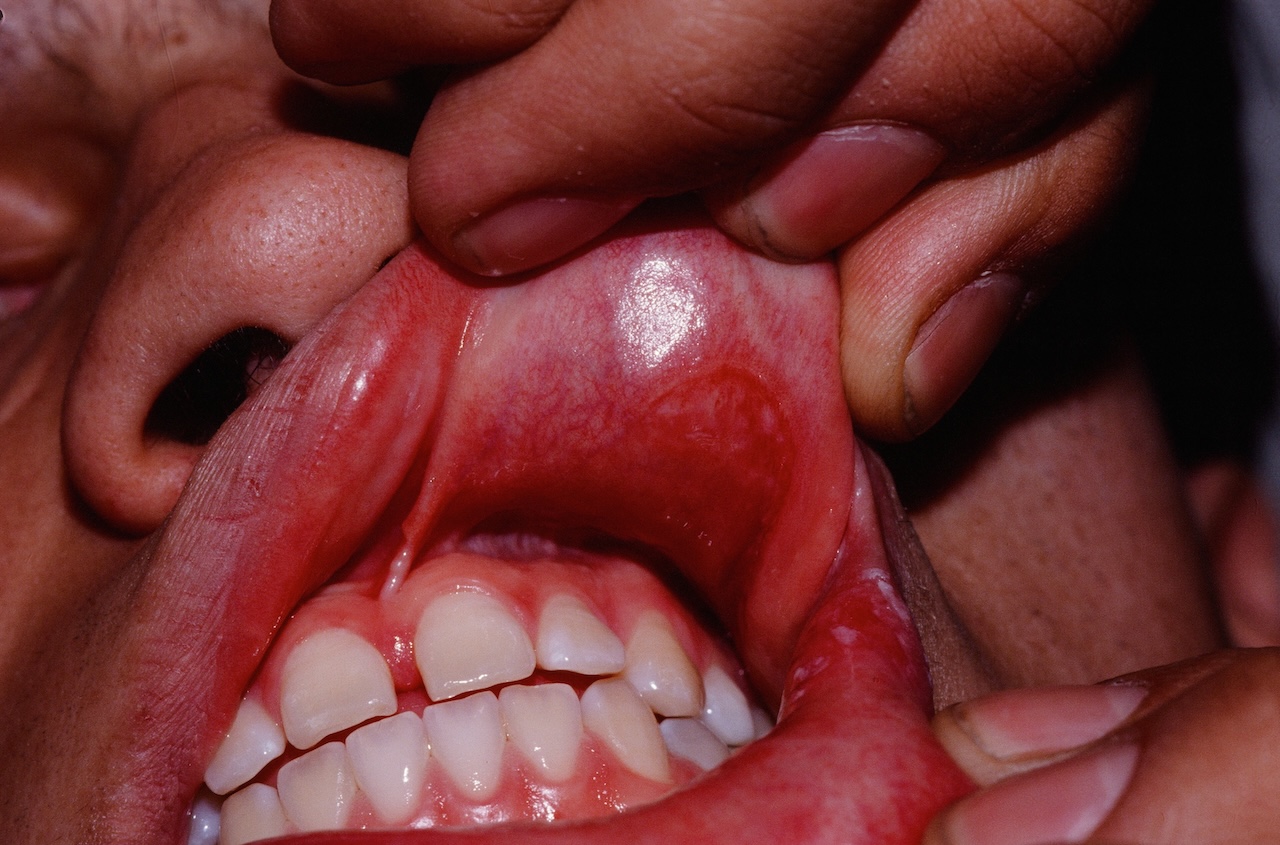
Mucous patches of secondary syphilis.
RegionalDerm
Who is Dr. White? | Privacy Policy | FAQs | Use of Images | Contact Dr. White
It is not the intention of RegionalDerm.com to provide specific medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. RegionalDerm.com only intends to provide users with information regarding various medical conditions for educational purposes and will not provide specific medical advice. Information on RegionalDerm.com is not intended as a substitute for seeking medical treatment and you should always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider for diagnosis and for answers to your individual questions. Information contained on RegionalDerm.com should never cause you to disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking treatment. If you live in the United States and believe you are having a medical emergency call 911 immediately.

