 It hurts!
It hurts!
SUNBURN
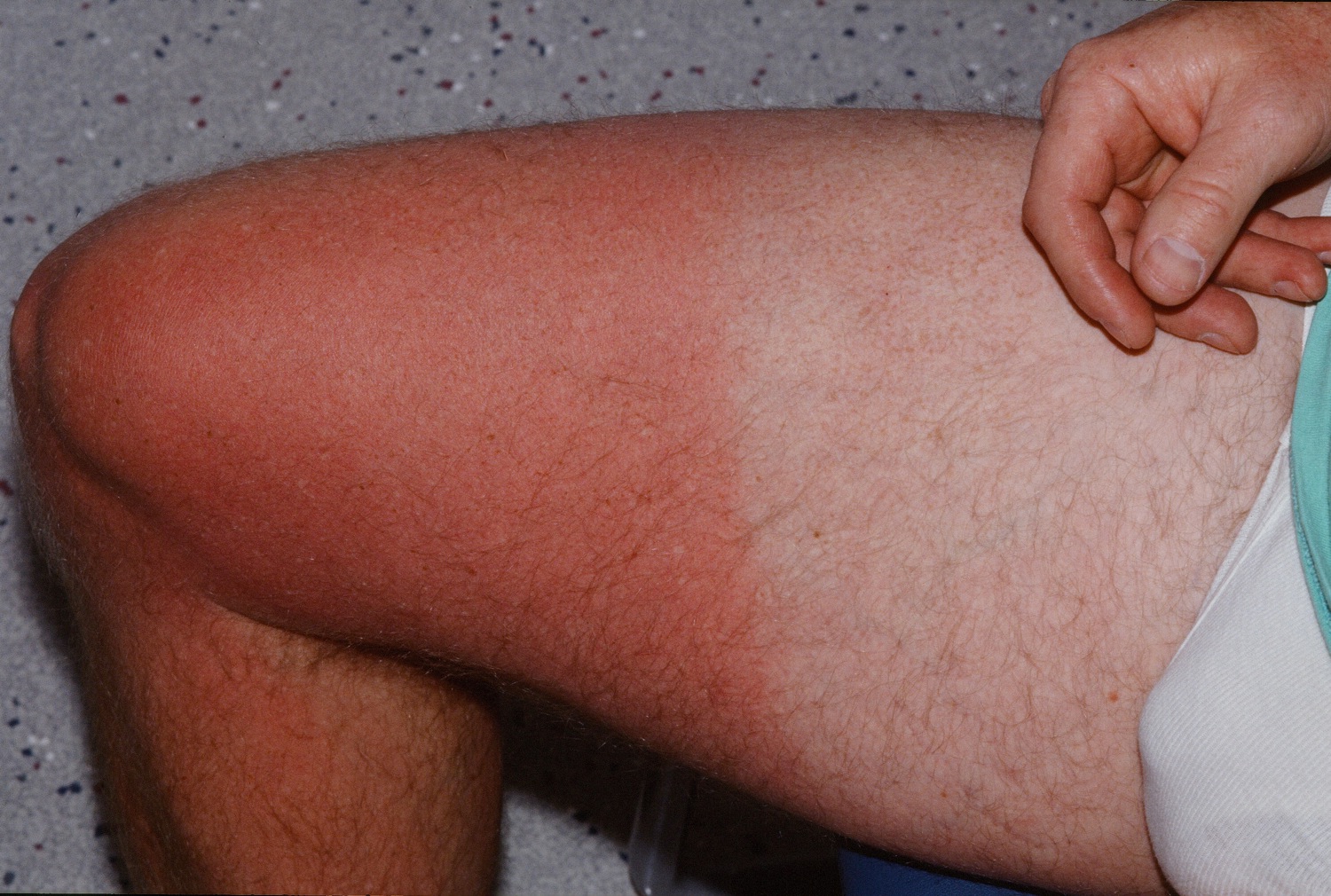
A sunburn is the reddening, inflammation, and, in severe cases, blistering and peeling of the skin caused by overexposure to the ultraviolet rays of the sun.
- Sunburns before the age of 20 are associated with more melanocytic and atypical melanocytic nevi, whereas in adulthood, sunburns tend to cause the development of actinic keratoses.
- Severe sunburns are linked to the development of BCC, SCC and melanoma.
- Being in the shade (and not using sunscreen) can still lead to sunburn.
- Factors associated with visits to the ER for sunburn in one study included psychiatric illness, alcohol use and homelessness.
Clinical
The skin becomes erythematous and tender in the areas of photo-exposure. Blisters may form. Later, desquamation occurs.
Prevention
240 mg BID of Polypodium Leucotomos extract [PLE] reduced the likelihood of sunburn in healthy adults in a RDBPCT. It also increased the minimal erythema dose. Similar findings were shown in a study that had subjects take 240 mg of PLE 2 hours and 1 hour before UV exposure. Of note, Heliocare is currently the preferred product available OTC in the US that contains PLE.
Sunburn Purpura
Sunburn purpura remains a rare phenomenon in which a petechial or purpuric rash develops acutely after intense sun exposure.
Additional Pictures
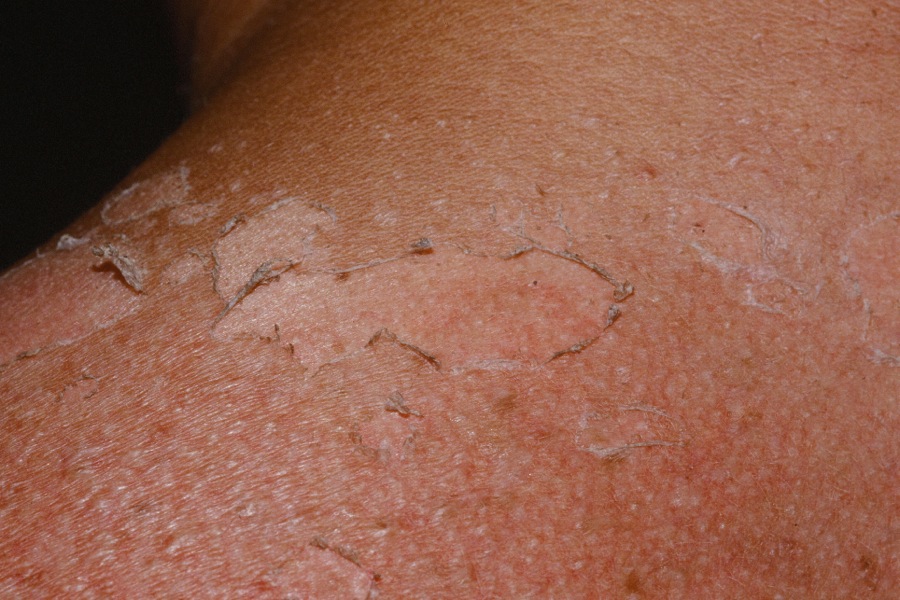
Desquamation is very common after a sunburn.
RegionalDerm
Homepage | Who is Dr. White? | Privacy Policy | FAQs | Use of Images | Contact Dr. White
It is not the intention of RegionalDerm.com to provide specific medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. RegionalDerm.com only intends to provide users with information regarding various medical conditions for educational purposes and will not provide specific medical advice. Information on RegionalDerm.com is not intended as a substitute for seeking medical treatment and you should always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider for diagnosis and for answers to your individual questions. Information contained on RegionalDerm.com should never cause you to disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking treatment. If you live in the United States and believe you are having a medical emergency call 911 immediately.
 It hurts!
It hurts!