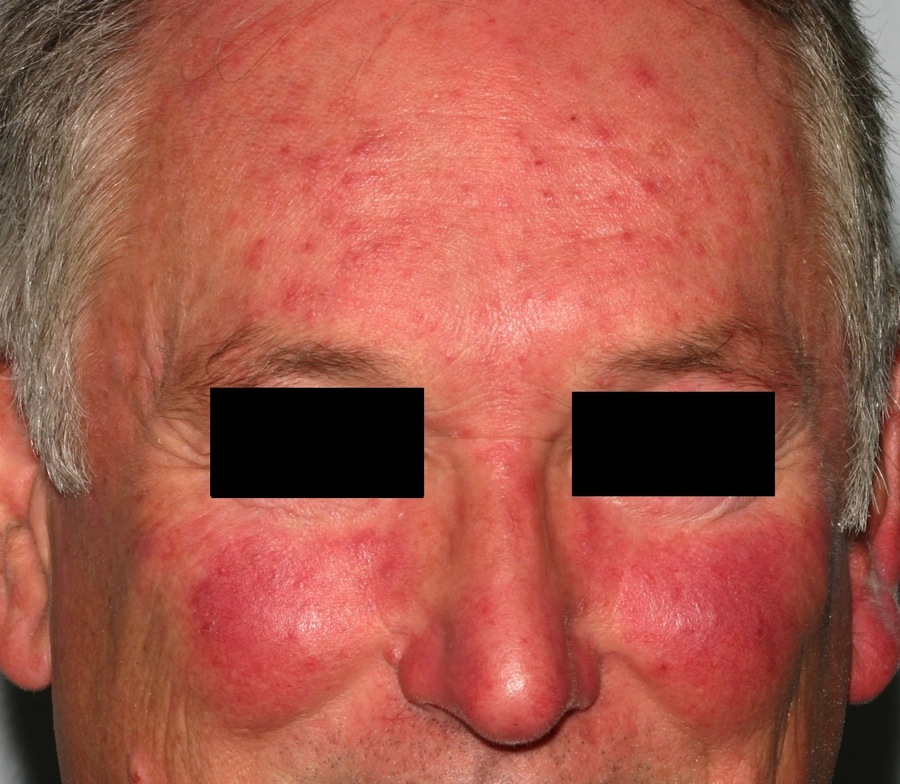
Inflammatory papules on the face and near confluent erythema of the nose and cheeks is typical of rosacea.
ROSACEA
Rosacea is a papular inflammatory eruption of the face in adults. It is not acne and this author prefers to avoid the term "acne rosacea." Red, inflamed papules and pustules develop on the nose and cheeks. Often there is a background of redness, superficial blood vessels (telangiectasias) and flushing. Hot foods or liquids, sun, and wind may trigger the flushing. Redness or blood vessels alone, without papules and pustules, is not rosacea.
- Rosacea seems to represent a mild surface infection or overgrowth by normal flora--particularly Demodex.
- Fair-skinned adults are preferentially affected.
- Patients with rosacea often have sensitive skin.
- Mask wearing aggravates all aspects of rosacea in the covered areas.
- Ocular rosacea may accompany rosacea. Signs include red or dry eyes. Symptoms include burning, stinging, light sensitivity, and foreign-body sensation.
- Woman with rosacea are more likely to have migraines.
- Chronic topical steroid use on the face may induce a rosacea-like eruption, so called steroid-rosacea.
General Measures
- Use a gentle skin care routine with unscented cleansers and moisturizers (e.g., Cetaphil, Dove Sensitive Skin, Cerave)
- Avoid cleansers with abrasive or exfoliating agents, alcohol, acetone, and scents.
- Allow skin to dry before applying any medication (or moisturizer).
- Always apply any prescription medication first, before any moisturizer or makeup.
- A green-tinted makeup can help reduce the appearance of redness.
- If flushing is a problem, triggers (e.g. hot foods or liquids) should be avoided as much as possible.

This is not rosacea, but surface blood vessels (telangiectasias). The pulsed-dye laser (e.g. Vbeam) can be excellent for these.
RegionalDerm
Who is Dr. White? | Privacy Policy | FAQs | Use of Images | Contact Dr. White
It is not the intention of RegionalDerm.com to provide specific medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. RegionalDerm.com only intends to provide users with information regarding various medical conditions for educational purposes and will not provide specific medical advice. Information on RegionalDerm.com is not intended as a substitute for seeking medical treatment and you should always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider for diagnosis and for answers to your individual questions. Information contained on RegionalDerm.com should never cause you to disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking treatment. If you live in the United States and believe you are having a medical emergency call 911 immediately.


