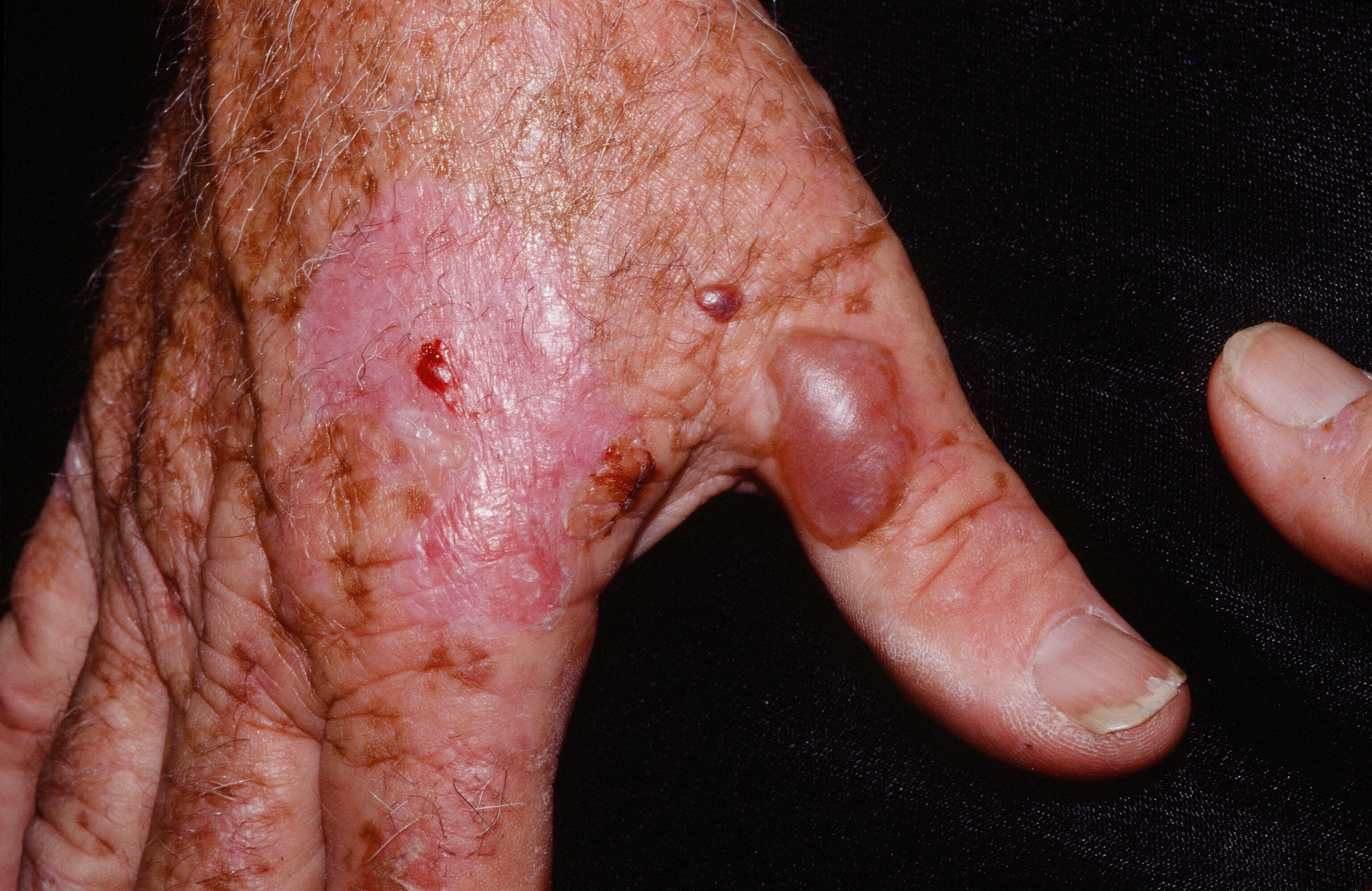
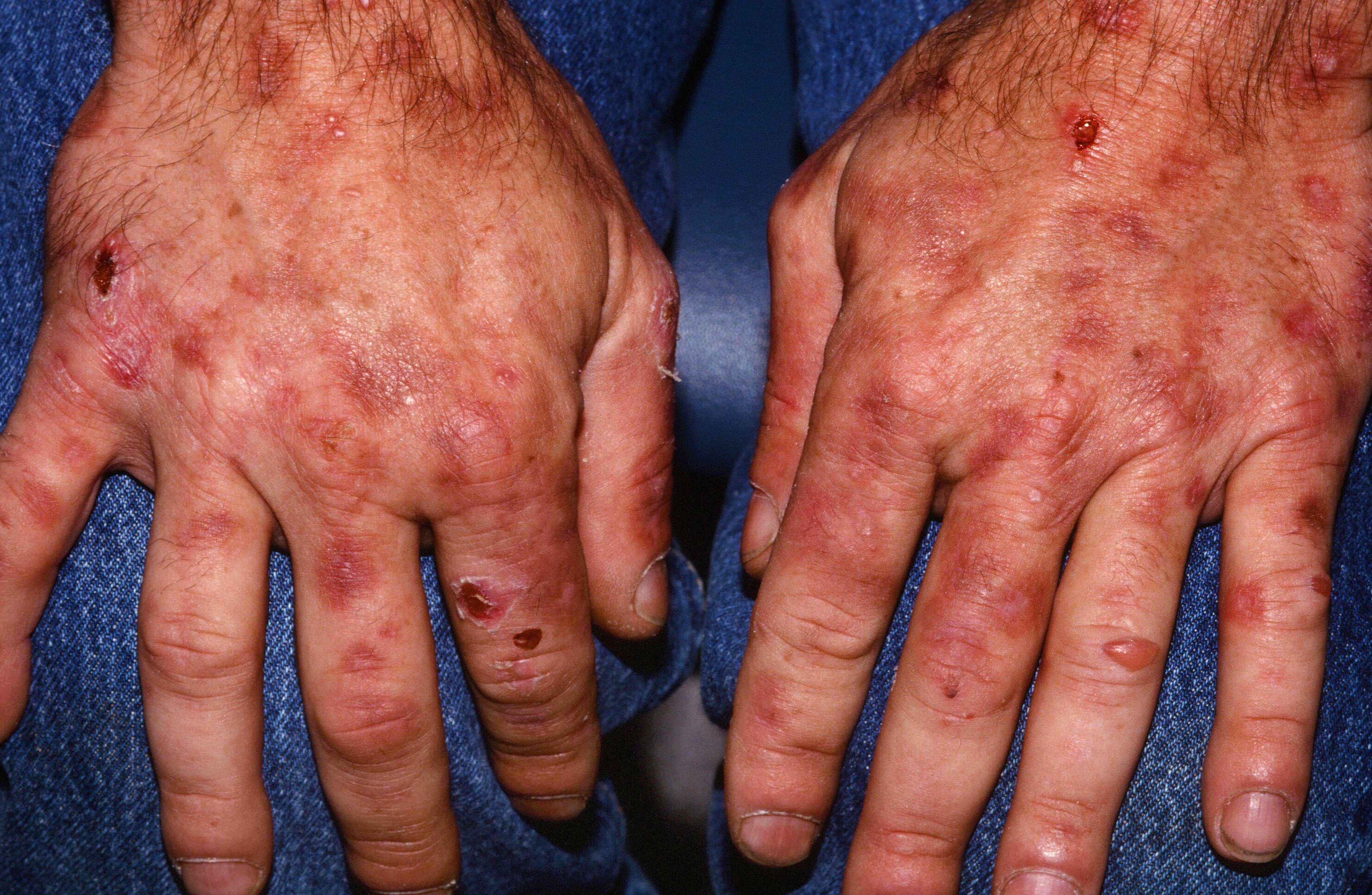
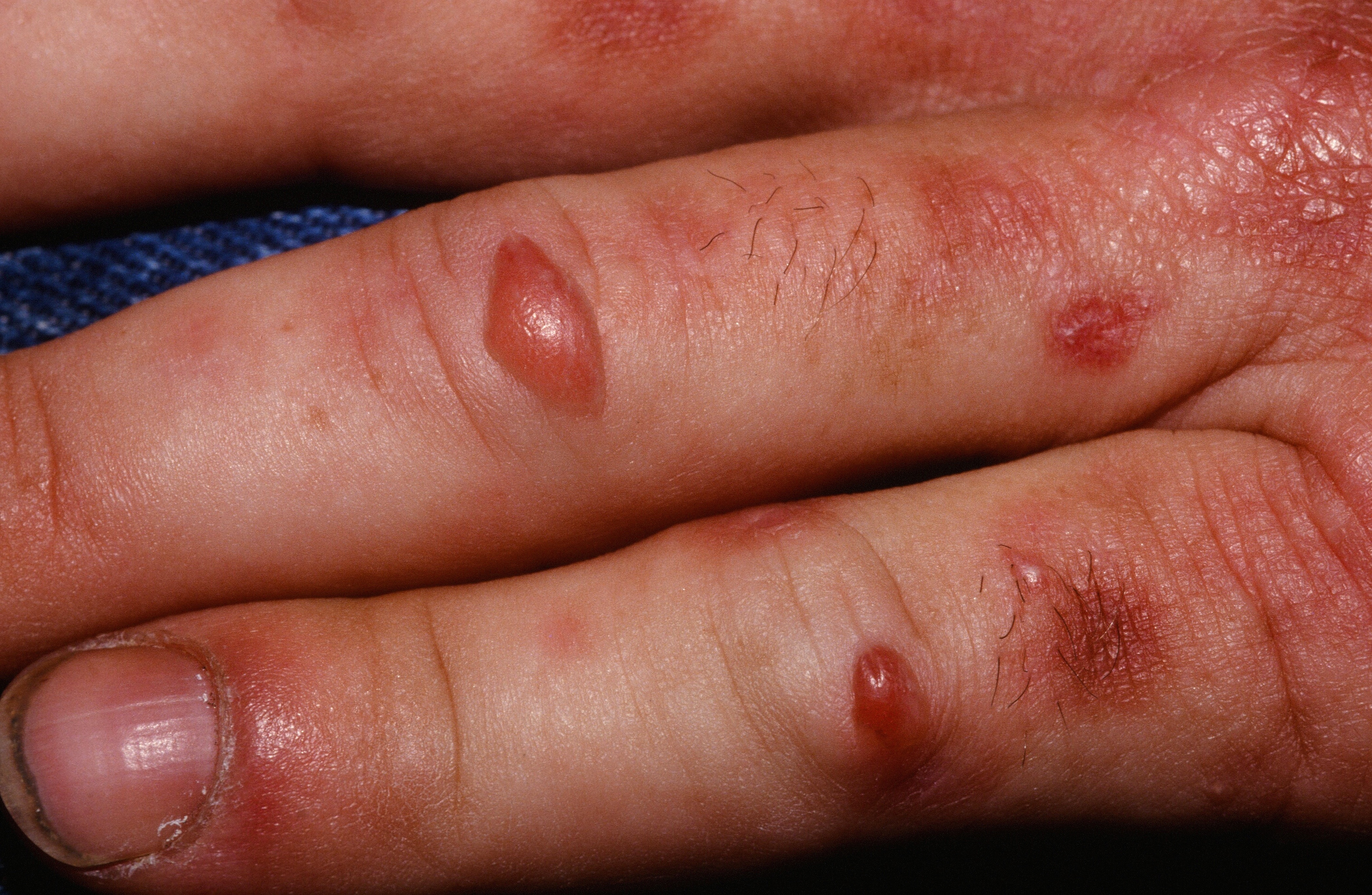
Blisters and skin fragility on the back of the hands is typical.
PORPHYRIA CUTANEA TARDA
Porphyria Cutanea Tarda (PCT) is a blistering disease, most common on the back of the hands caused by sun exposure and build up in the blood of porphyrins.
- Both an inherited (AD) and an acquired type have been described. For both types, uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase functional activity is low, and a history of exposure to alcohol, estrogens (e.g. oral contraceptives for women or estrogen for prostate cancer in men) or other liver toxic agent (e.g. drug) may be found.
- In one study, Hepatitis C virus antibodies were found in 79% of patients with acquired PCT and in none with familial PCT. The connection between PCT and Hepatitis C varies tremendously by geographic location. For example, the presence of HC in PCT patients has been reported as follows: Indiana (in the US) 94%, Southern Europe 65%, Australia/New Zealand 20%, Northern Europe 17%.
- Hepatocellular carcinoma may cause PCT as a paraneoplastic manifestation. Removing the carcinoma causes resolution of the symptoms.
- Mutations causing hemochromatosis are more common in patients with PCT.
- Patients with PCT have an increased mortality, primarily explained by an increased mortality from gastrointestinal diseases and from cancers of the gut, liver/gallbladder, and lungs.
Clinical
Vesicles, milia, erosions and fragile skin occur symmetrically on the dorsa of the hands in porphyria cutanea tarda. Look for hypertrichosis along the forehead. In rare cases, usually when the disease goes for a long time untreated, indurated, sclerodermoid plaques may develop on the trunk. The hematocrit is often elevated.
Differential Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made by measuring urinary porphyrins and excluding VP through measurement of fecal porphyrins. PCT may develop in the setting of renal failure and dialysis. Finally, a bullous dermatosis mimicking PCT (pseudoporphyria) but without elevated porphyrin levels may also occur in dialysis patients. This type may be related to various drugs (e.g. furosemide, nalidixic acid and tetracycline).
Drugs and PCT
So, to clarify, a drug may cause PCT which on workup would show elevated porphyrins. Or, a drug could cause pseudopct which would not show elevated porphyrins. But the clinical picture (e.g. blisters and vesicles on the back of the hands) is the same.
RegionalDerm
Who is Dr. White? | Privacy Policy | FAQs | Use of Images | Contact Dr. White
It is not the intention of RegionalDerm.com to provide specific medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. RegionalDerm.com only intends to provide users with information regarding various medical conditions for educational purposes and will not provide specific medical advice. Information on RegionalDerm.com is not intended as a substitute for seeking medical treatment and you should always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider for diagnosis and for answers to your individual questions. Information contained on RegionalDerm.com should never cause you to disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking treatment. If you live in the United States and believe you are having a medical emergency call 911 immediately.

