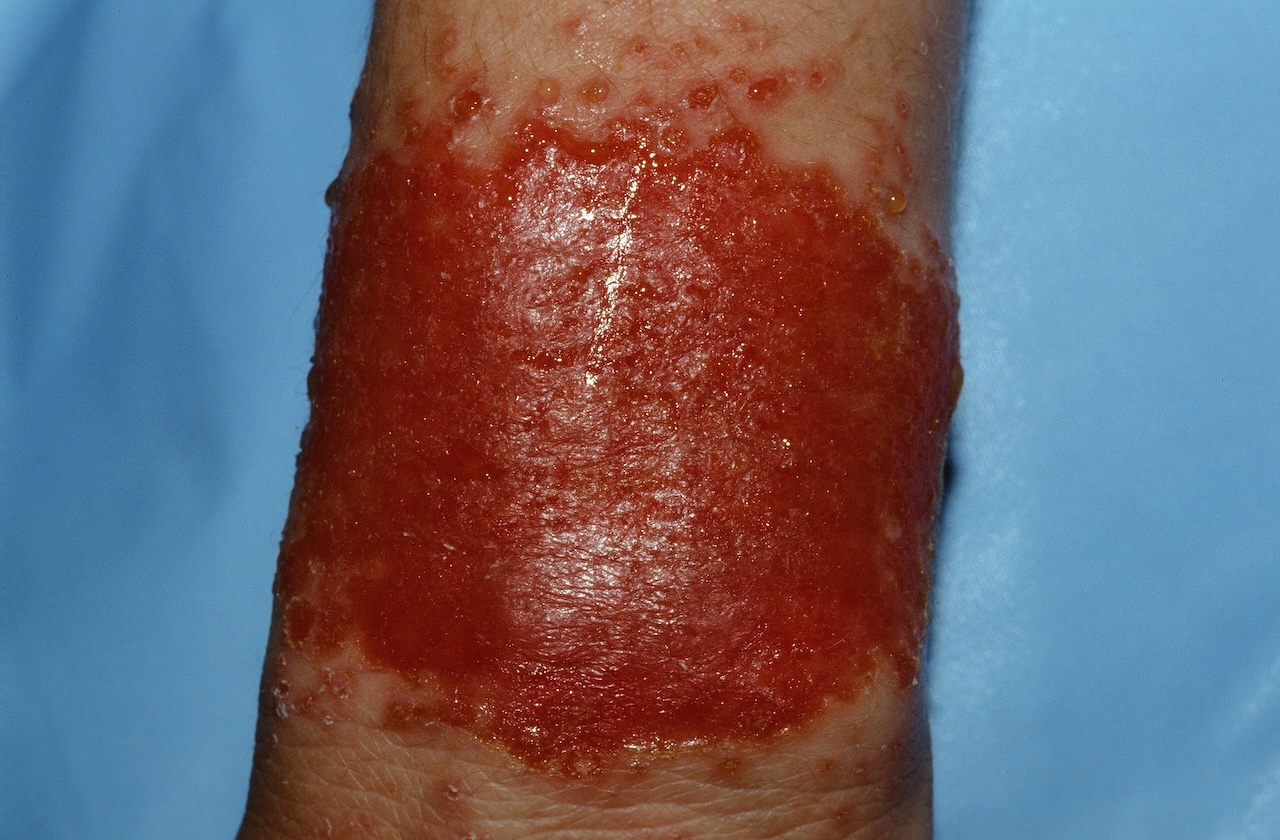
This patient was treated by primary care with keflex without improvement. Adding diprosone ointment cleared the rash in 10 days.

This patient was treated by primary care with keflex without improvement. Adding diprosone ointment cleared the rash in 10 days.
The coexistence of an eczema and skin infection by Staphylococcus is common. When the bacterial infection is the inciting process and the eczema develops from it, the term "infectious eczematoid dermatitis (IED)" is used. When the eczema occurred first and the bacterial infection is secondary, the term "impetiginized eczema" is used. Sometimes, it is hard to know which started first.
In IED, vesicles and pustules radiate out from an infected site. In impetiginized eczema, the skin first is red, scaly, and eczematous, and then becomes moist, oozy, weepy, and crusting. The end result is often the same--a moist, red, oozing plaque. The edges are ill-defined, microvesicular, and the process spreads outward over time. Itching is common.
Eczema herpeticum (EH) should always be considered in the differential. In EH, tiny crusted circles or erosions representing eroded vesicles are often visible, especially at the periphery.
Homepage | Who is Dr. White? | Privacy Policy | FAQs | Use of Images | Contact Dr. White