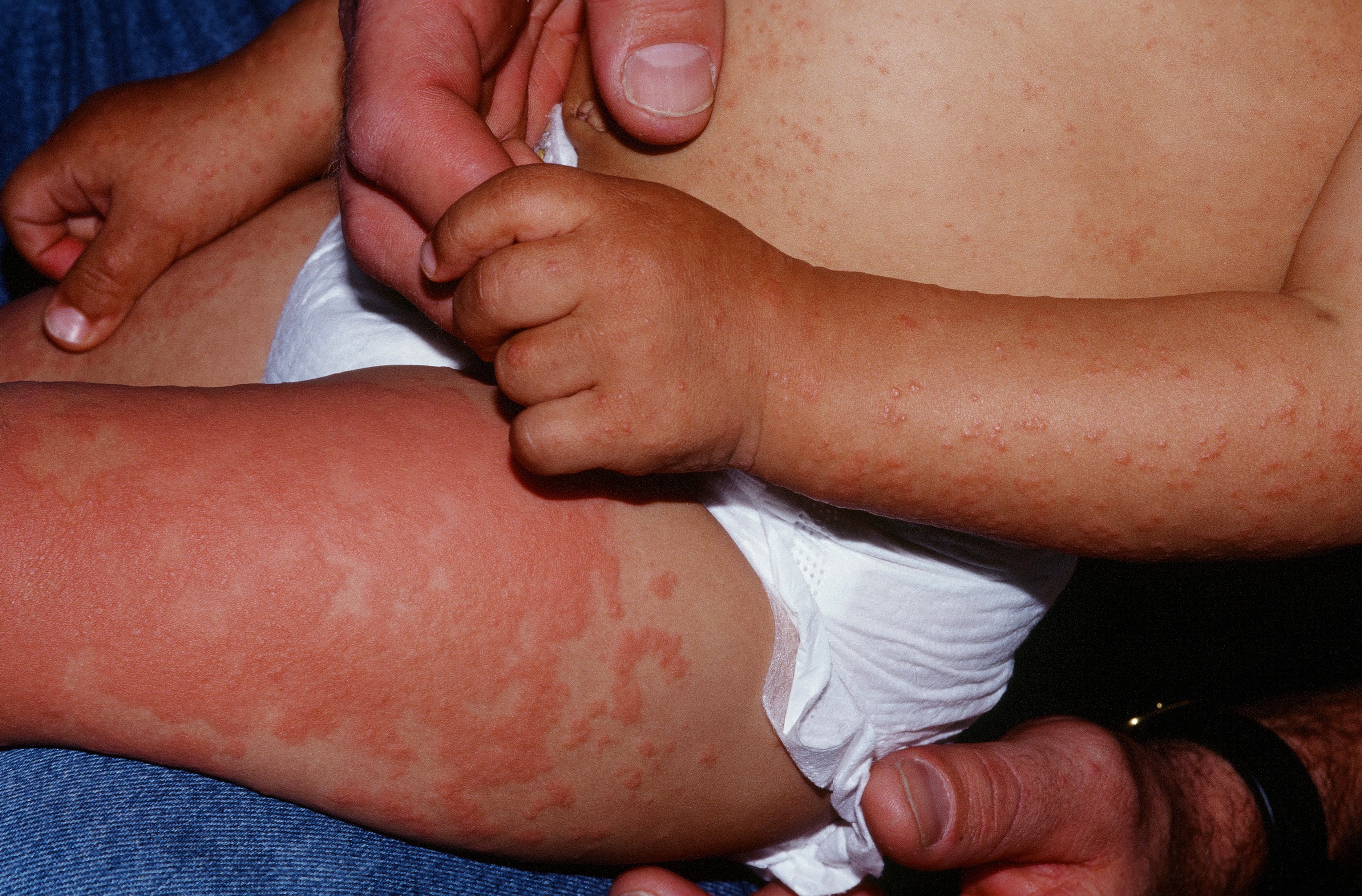
3 yo with a diffuse papular rash.

3 yo with a diffuse papular rash.
Papular acrodermatitis of childhood (PAC), also known as Gianotti-Crosti Syndrome (GCS), is a self-limited disorder with acute onset generalized lymphadenopathy and a symmetric erythematous papular and papulovesicular eruption of the face, neck, buttocks, and extremities, usually occurring in young children. This rash seems to result from an underlying viral infection, and has been noted to occur in association with molluscum, hepatitis B, varicella, coxsackie virus, CMV, enterovirus, hepatitis A, herpes simplex 1 virus and Epstein-Barr viruses.
The patient presents with symmetric, inflammatory red papules and plaques on the face, buttocks, extensor forearms and extensor legs. In some patients, the papular eruption is quite prominent on the elbows and knees. It tends to spare the trunk and is not scaly. In contrast to a viral exanthem, it tends to last > 10 days and often many weeks. Lymphnodes may be enlarged. Linear lesions from Koebnerization occur.
GCS-like reaction (GCLR) is a similar condition that presents as a hypersensitivity reaction in response to molluscum contagiosum. Although the rash closely resembles that of GCS, GCLR can be distinguished in that lesions are frequently accompanied by severe pruritus and localized over extensor surfaces of large joints in the presence of a concurrent MC infection.
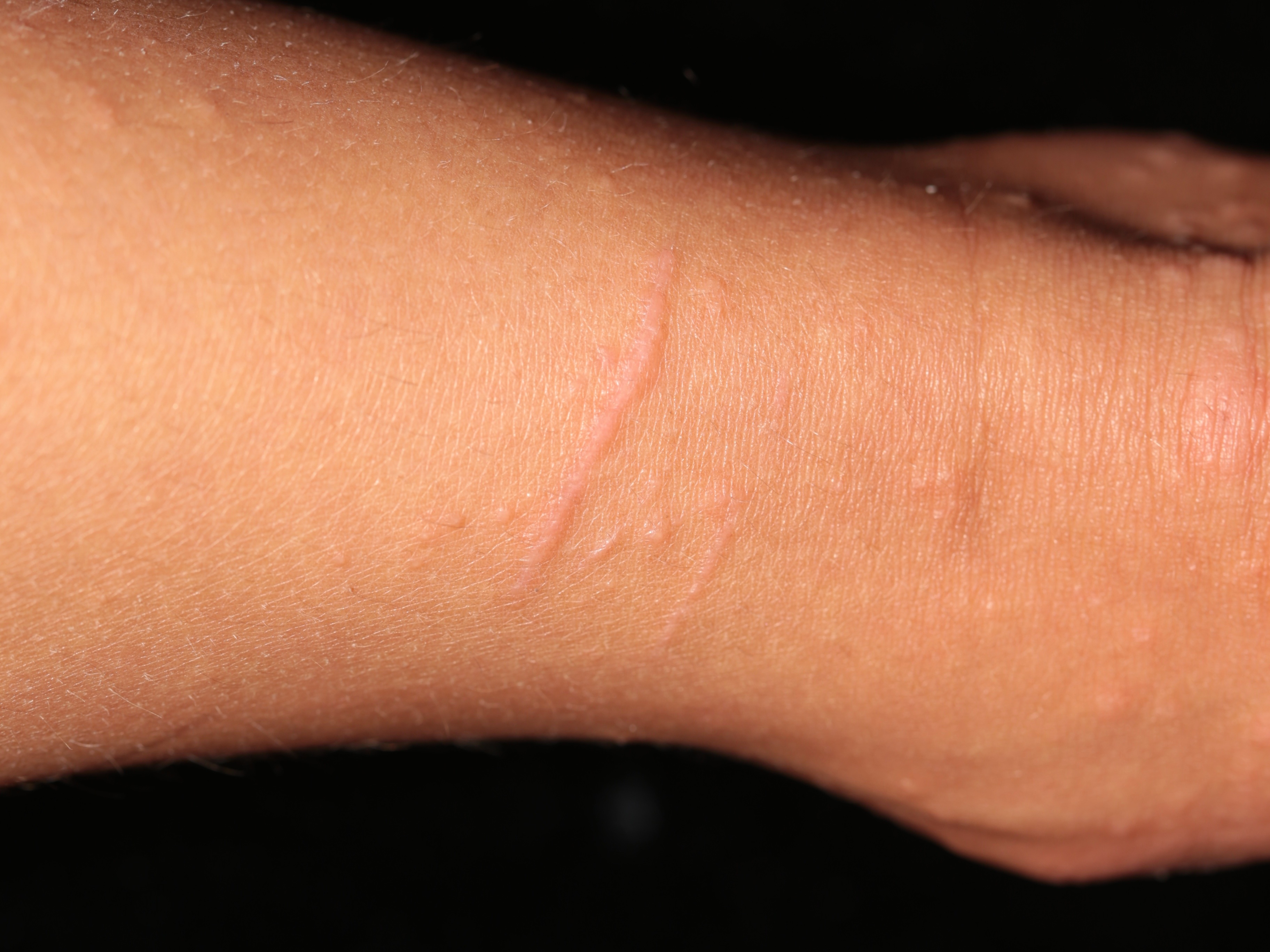

Linear lesions of GCS showing Koebnerization.
Homepage | Who is Dr. White? | Privacy Policy | FAQs | Use of Images | Contact Dr. White