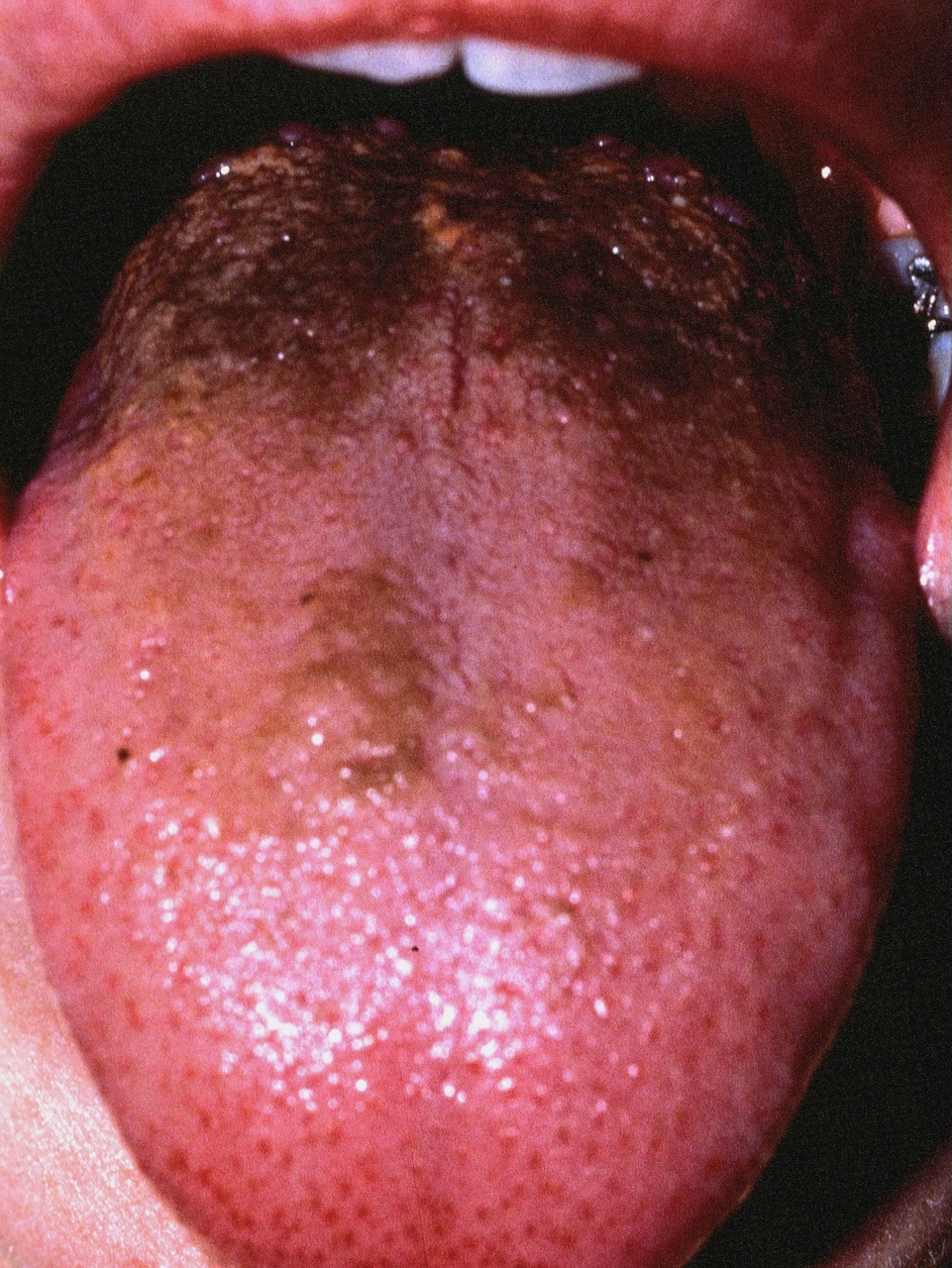
BLACK HAIRY TONGUE
Black hairy tongue (BHT) is a benign discoloration of the dorsal surface of the tongue. Excessively long filiform papillae are black in color due to accumulation of keratin and chromogenic microorganisms.
- The condition usually occurs in older individuals but infants as young as 2 months of age may be affected.
- Common contributing factors include poor oral hygiene, regular use of oxidizing mouthwashes, dry mouth, antibiotic use, tobacco, coffee, tea, alcohol, and eating mainly soft foods.
- Some oral antibiotics can precipitate a black, hairy tongue by altering the microflora of the oral mucosa. Reported offenders include the tetracyclines (like doxycycline and minocycline), erythromycin, penicillins, linezolid, and amoxicillin-clavulanate.
- Taking bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol) can induce it as well.
BHT occurs because of a buildup of keratin cells, which are the proteins that also make up human hair. This buildup can give the tongue a rough, hairy texture. This rough surface also provides an excellent area for bacteria and fungi to multiply, which could also cause a green tongue.
Clinical
The dorsal surface of the tongue is blackened. The filiform papillae are long and dark in color.
RegionalDerm
Who is Dr. White? | Privacy Policy | FAQs | Use of Images | Contact Dr. White
It is not the intention of RegionalDerm.com to provide specific medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. RegionalDerm.com only intends to provide users with information regarding various medical conditions for educational purposes and will not provide specific medical advice. Information on RegionalDerm.com is not intended as a substitute for seeking medical treatment and you should always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider for diagnosis and for answers to your individual questions. Information contained on RegionalDerm.com should never cause you to disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking treatment. If you live in the United States and believe you are having a medical emergency call 911 immediately.
