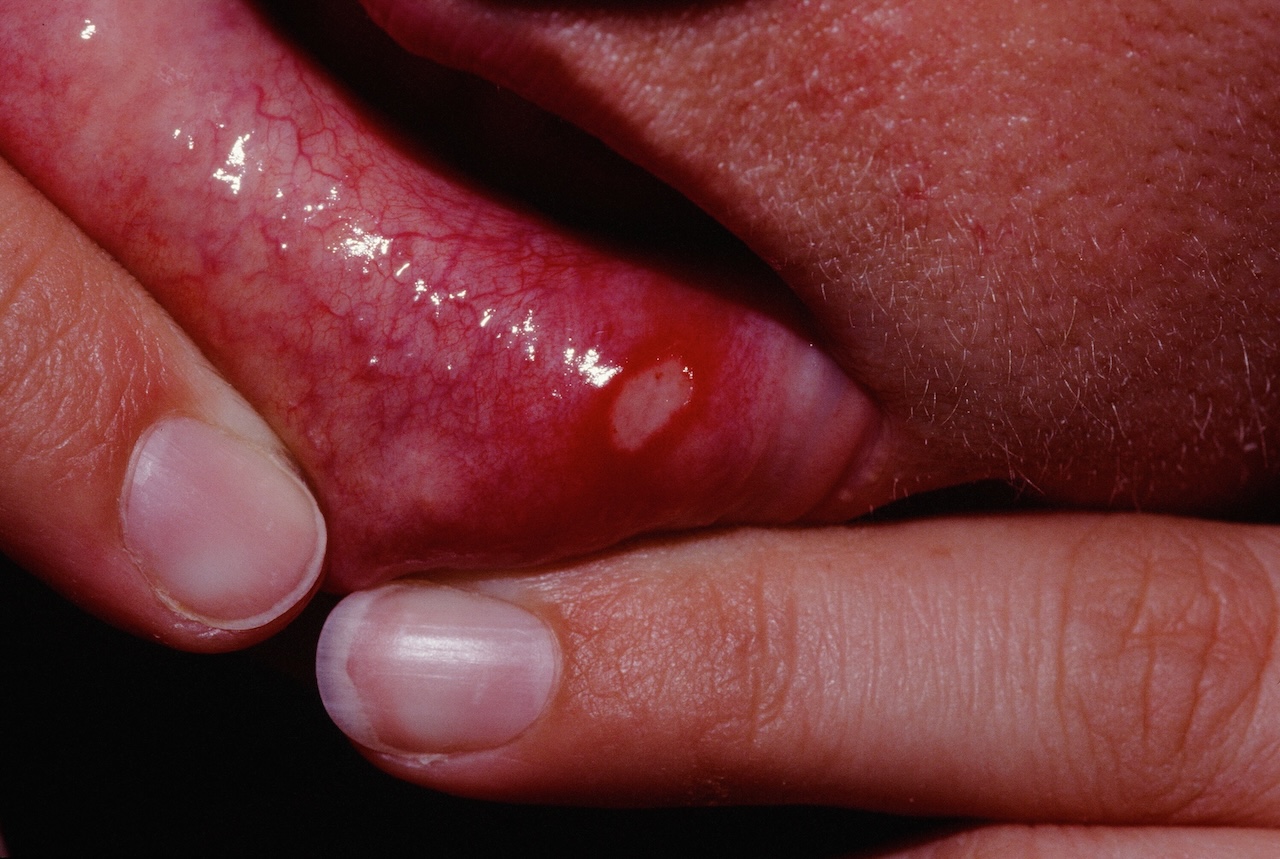
Aphthous ulcers (AU) are painful superficial oral erosions. They often come in crops. Trauma may induce them. The majority of cases are idiopathic.
Aphthous ulcers appear as white or gray oval areas with a bright red surrounding erythema in the oral cavity. They most commonly occur on the buccal and labial mucosa.
Occasionally, patients may have a more severe presentation with larger or more persistent lesions. The term major aphthous stomatitis has been used and is defined as ulcers greater than 1 cm that are present for more than two weeks and often heal with scarring.
Some have suggested that recurrent aphthous stomatitis may have an immunogenetic background owing to cross-reactivity with the bacteria Streptococcus sanguis (a normal inhabitant of the healthy human mouth). A small percentage of patients have a deficiency (e.g., iron, folate, vitamin B-12). There are isolated case reports of zinc deficiency and fluoride allergy.
PFAPA (Periodic Fever, Aphthous Stomatitis, Pharyngitis, Adenitis) is a childhood syndrome that affects both boys and girls. It causes repeated episodes of fever, mouth sores, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes. PFAPA usually starts in early childhood between ages 2 and 5.
Many triggers have been reported including spicy foods, citrus, walnuts, pineapple, trauma (e.g., from the toothebrush, self-biting, dental procedures), menstruation, pregnancy, menopause and stress.
Blood work for HIV, iron, zinc, folate and vitamin B12 may be measured. The history may be reviewed for inflammatory bowel disease or any signs of other skin problems, e.g. vasculitis, genital ulcerations (Behcets Syndrome).
Homepage | Who is Dr. White? | Privacy Policy | FAQs | Use of Images | Contact Dr. White